May 17, 2025 | 18:16 GMT +7
May 17, 2025 | 18:16 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
May 17, 2025 | 18:16 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
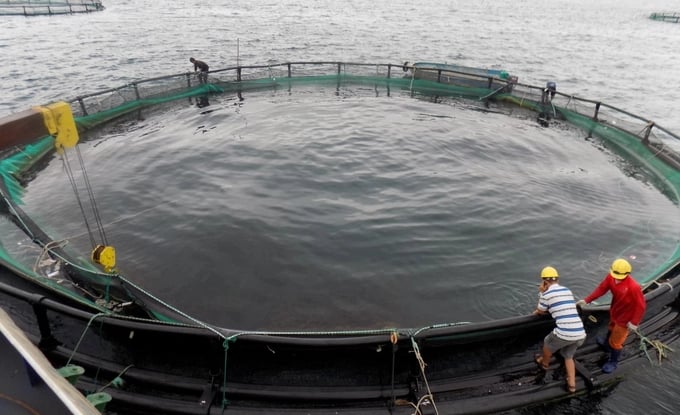

Vietnam has a long coastline with many islands, bays, and lagoons, which are advantages for offshore mariculture. Photo: K.S.
For many years, coastal aquaculture in our country has been developing rapidly, creating jobs for local communities, promoting socio-economic development, and increasing export output. The coastal aquaculture systems are mainly small-scale, household, and rudimentary cage materials. Farmed species such as marine fish, lobster, mollusks, and seaweed are diverse.
The rapid development of coastal aquaculture has led to many consequences, such as environmental pollution, disease spread, narrow coastal space and sometimes conflicts with other economic sectors such as tourism and real estate. In that context, expanding the space for mariculture and moving farms away from the shore is one of the solutions that have been noticed.
Offshore mariculture is usually defined as six nautical miles or more from the coastline. In offshore waters, it will be less affected by estuarine alluvium, rich and diverse plankton ecosystems, ample space, stable depth, flow, clarity, temperature, and salinity. However, farms will also be affected by waves and stronger winds than in coastal areas.
Vietnam has a coastline of more than 3,260km, extending from Quang Ninh to Ca Mau and Kien Giang, along with thousands of large and small islands in the sea, many pools, bays, lagoons and lagoons, suitable for mariculture industry development that not every country has. Vietnam's exclusive marine economic zone is over 1 million square kilometers, accounting for about 30% of the East Sea area. According to a study by Nha Trang University, there are 3 favorable areas for offshore mariculture development, namely Quang Ninh, Khanh Hoa and Kien Giang, based on the criteria of environment, depth, current, and degree of water saltwater, and especially there are islands that are sheltered from wind and storms.

Over time, people in the South Central Coast have revealed many inadequacies, affecting economic efficiency due to many diseases. Photo: K.S.
In our country, offshore mariculture has not been thoroughly studied. This is a new industry not only for Vietnam but also in the world. Therefore, offshore mariculture requires more research, careful planning, and comprehensive policies to ensure efficiency, safety, and sustainability. Offshore marine ecosystems are significantly different from nearshore.
When offshore mariculture flourishes, ecosystems and marine life will be more or less affected. In the long term, the impacts of mariculture on the marine environment, ecology and space can hardly be fully assessed, as well as the potential risks that are difficult to predict because we do not have enough data and scientific data pilot models.
The sea of our country is regularly affected by storms, winds, and tropical depressions with high frequency. The North Sea is affected by a long cold winter, which is detrimental to production. In the context of climate change, Vietnam is one of the most vulnerable countries. The number of large and extreme storms in the East Sea shows signs of increasing. The farming time is extended, with marine fish 12-15 months/crop, lobster 18-20 months/crop, significant investment capital, high production risk, and incomplete mariculture insurance policy leading to limited economic sectors participating in mariculture.
The development of offshore mariculture requires an entirely new and systematic approach. The basic premises include integrated infrastructure, logistics, human resources, seed, feed, services and materials, national and international legal frameworks, economic issues, and social, political, oceanographic, biological, environmental, and technological criteria.
It isn't easy to build a complete set of criteria because most factors are interactive and not fixed but interdependent. For example, sea level depth is related to the velocity of ocean currents. In addition, the selection of suitable farming sites must meet the standards or depend on the technology and depending on the species.
Climate change can affect ecological risks such as changes in migration, abundance and distribution of species. Therefore, these changes should also be included in the sets of criteria, standards and regulations on offshore mariculture.
Regarding technology, the type of cages, nets, buoys and mooring lines must withstand harsh weather conditions, high waves and strong currents. Cage materials must be stable, reliable, capable of inhibiting algae growth, and resistant to corrosion and fouling.
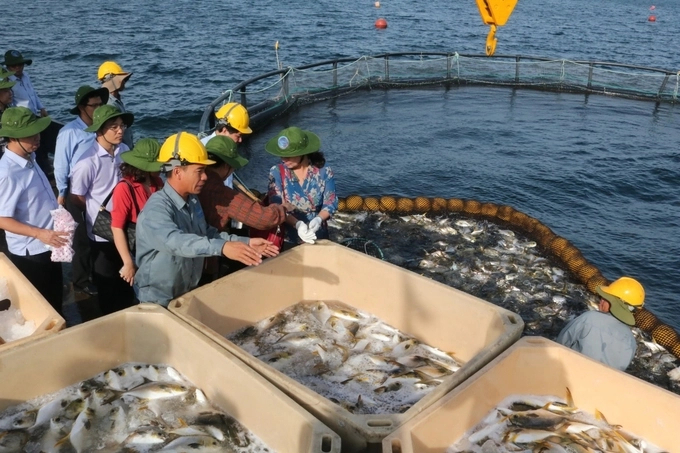

Breeding industrial yellowfin pompano in Van Phong Bay using HDPE cage technology. Photo: K.S.
Farmers are not always present in the cage in an environment far from land, especially during storms or tropical depressions. Therefore, most of the daily tasks of farmers will have to be replaced by machines, which are automatically and remotely controlled, for example, automatic feeding technology, automatic washing facilities to clean the net, or management, care, and harvesting measures through intelligent control systems.
Producing fingerlings of marine fish in our country is still limited. The hatcheries usually operate on a small scale. The facilities and technology are still outdated, the breed quality is unstable, and many breeding herds are at risk of inbreeding. The lack of breed production also affects the development of commercial farming on an industrial scale. Aquaculture workers lack knowledge of science and technology and lack experience in managing and operating offshore farms.
Waste from marine farms, such as leftovers, fish manure and domestic waste, will disperse quickly in the aquatic environment or sink as soon as pellets. This will organically enrich the bottom sediments in the vicinity of the farm. The benthic response to organic enrichment cannot be assessed.
In offshore waters, few benthic animals can tolerate pollution, so the ability of benthic organisms to assimilate organic matter may be limited. Instead, the decomposition of the wastes will be done by microorganisms, leading to increased oxygen demand and accumulation of sulfide in the sediment. This can negatively affect benthic biodiversity.
Offshore mariculture is predicted to thrive in the next few decades as the coastal space exposes its limitations and pollutes the environment or is prioritized for developing other critical economic sectors. Are existing management tools suitable for the offshore industry, or must they be updated and reinforced with some pilot models?
Is the current aquaculture human resource sufficient for industrial farming in the open sea, or does it need retraining? Standards and regulations for forming offshore marine farms that meet the national and international legal framework..., are issues that need to be discussed and considered.
Translated by Ha Phuc

(VAN) Minister of Agriculture and Environment Do Duc Duy held a meeting with Soopakij Chearavanont, Chairman of C.P. Group, on May 15.
/2025/05/16/3800-0-nongnghiep-143756.jpg)
(VAN) Suntory PepsiCo Vietnam coordinated with the Ministry of Education and Training to implement an education program on water conservation, reaching nearly 1 million primary school students nationwide.

(VAN) Vietnam’s TH Group officially put its high-tech fresh milk processing plant into operation in the Russian Federation, marking a historic moment as the first TH true MILK cartons were produced in Russia.
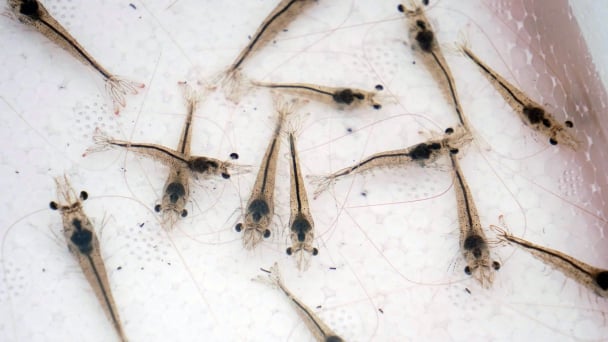
(VAN) Use of high-quality broodstock and biotechnology is regarded as the most effective approach to ensuring sustainable and economically viable shrimp aquaculture ahead of climate change and the emergence of increasingly intricate disease patterns.

(VAN) Carbon farming is a form of agricultural practices that helps absorb more greenhouse gases than it emits, through smart management of soil, crops, and livestock.

(VAN) This is a key content of the Memorandum of Understanding recently signed between the Vietnam Fisheries Society and Kunihiro Inc of Japan.

(VAN) To achieve the goal, local authorities and businesses in Kon Tum province have fully prepared the necessary conditions for the new Ngoc Linh ginseng planting season.