June 29, 2025 | 08:37 GMT +7
June 29, 2025 | 08:37 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
June 29, 2025 | 08:37 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
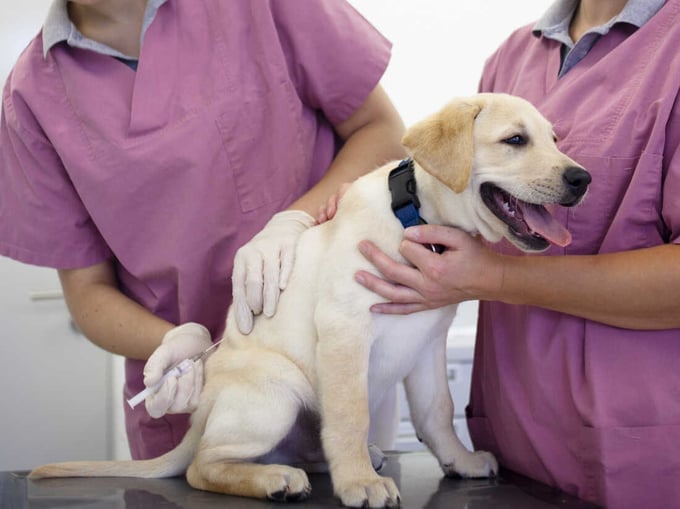
The Ministry of Health demands local governments to implement various measures for the prevention and control of rabies. Photo: GI.
According to a report from the infectious disease surveillance system under the Ministry of Health, the number of recorded rabies cases has been on a steady rise since 2022. Notably, multiple provinces and cities have experienced a persistent circulation of the disease over several years at a relatively high mortality rate.
There has been a noticeable increase in rabies cases since the beginning of 2024; 22 deaths have resulted from the disease, which is twice as many as in 2023 (10 cases). Namely, recent cases have been reported with short incubation periods, ranging from 10 to 15 days. The majority of reported cases involve children under 5 years old who were bitten by dogs or cats on the head or face, causing severe injuries in areas near the central nervous system.
The primary cause of rabies-related deaths in humans is the failure to receive vaccination in time following a bite of a suspected rabid animal. Public awareness regarding the dangers of rabies and preventive measures is relatively limited.
Additionally, several regions employ a lenient management of dog and cat populations, with a low vaccination coverage rate at only approximately 50%, leading to an increase in rabies cases in animals.
According to a report from the Department of Animal Health under the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development, 347 cases of rabies in animals were recorded across 31 provinces and cities in 2023. Additionally, 45 cases have been reported across 22 provinces and cities since the beginning of 2024. This is an increase of 6 cases, and two times higher than the number of affected provinces and cities compared to the same period in 2023.
In response to the rise in rabies cases, the Ministry of Health requested local governments to implement the contents of the National Rabies Prevention and Control Program from 2022 to 2030 in an urgent and effective manner.
It is imperative to closely monitor cases of suspected rabid animal bites to provide timely vaccination in accordance with the Ministry of Health's guidelines, and to promptly handle outbreaks. Strengthening inter-sectoral collaboration between health and veterinary sectors is necessary to detect cases of suspected rabid animal bites in time.
Accordingly, the related parties must ensure sufficient access to rabies vaccines and rabies immune globulin, with a focus on high-risk areas by allocating at least one vaccination center per district. Furthermore, they must consider establishing additional vaccination centers in remote regions. Healthcare professionals at vaccination centers should receive training on counseling skills and managing cases of animal bites.
On the other hand, local governments must strengthen communication efforts to raise awareness regarding the dangers of rabies, promptly disseminate information to encourage residents to take preventive measures and make timely visits to healthcare facilities for examination, counseling, and rabies vaccination, with a focus on areas with high mortality rates from rabies and low vaccination coverage rates for dogs and cats.
Other important activities include strengthening communication efforts for children and students; deploying public awareness campaigns; conducting direct communication and communication through the grassroots PSA systems in remote, rural, and ethnic minority-inhabited areas; providing warnings against treatment of rabies with methods not approved by the Ministry of Health.
The Ministry of Health also suggested local governments to allocate funds to implement rabies prevention and control activities for humans and animals in an effective manner, and mobilize the participation of committees, departments, organizations, and communities in rabies prevention and control efforts.
Translated by Nguyen Hai Long

(VAN) ECOEYE Korea expressed interest in cooperating with Vietnam in transferring advanced recycling technologies and developing the carbon market.

(VAN) At the SB62 Conference, the Vietnamese negotiation delegation engaged with several partners to promote cooperation on climate change response in Vietnam.

(VAN) Deputy Minister of Agriculture and Environment Hoang Trung emphasized the need for a comprehensive plan for the crop production sector to reduce emissions.

(VAN) International policies show that food system transformation cannot be separated from social inclusiveness, cross-sectoral integration, and multi-stakeholder coordination.

(VAN) Vietnam and China are strengthening connectivity and cooperation in the field of crop varieties and agricultural materials, paving the way for sustainable development in the agricultural sectors of both countries.

(VAN) Over the past 20 years, Hai Phong has reduced the number of bears in captivity from 500 to just over 10, thanks to the efforts of the forest protection force.

(VAN) Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh held talks with Chinese Premier Li Qiang on June 24, in Tianjin, China.