May 14, 2025 | 07:09 GMT +7
May 14, 2025 | 07:09 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
May 14, 2025 | 07:09 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918

The meeting was co-chaired by Mr. Vu Thanh Liem, Deputy Director of the International Cooperation Department under MARD, and Dr. Fred Unger, ILRI's Regional Representative for Asia. Photo: Linh Linh.
Mr. Vu Thanh Liem emphasized that the Human Health Protection through the One Health Approach in Vietnam project was funded by the CGIAR Trust Fund through ILRI. The initiative's objective is to enhance the detection, prevention, and management of foodborne maladies, zoonotic diseases, and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in order to protect human health.
MARD's leadership in the advancement of the One Health Partnership Framework to combat zoonotic diseases was underscored by Dr. Fred Unger. This framework has engaged stakeholders in the collaborative implementation of tasks, such as the One Health Initiative of the CGIAR, which addresses the intersection of environmental, animal, and human health. The project was co-led by the National Institute of Veterinary Research (NIVR) and ILRI, who fulfilled the responsibilities stated in the approved project documents. To date, the project has successfully achieved its objectives and has been completed within the set timeframe.
The One Health Initiative was implemented in six provinces and cities: Lao Cai, Hanoi, Thai Nguyen, Thua Thien - Hue, Dong Nai, and Can Tho. The initiative concentrated on three primary components.
Research on wildlife value chains and the identification of pathogens such as Hantavirus and Hepatitis E were conducted in local agencies for the initial component of zoonotic disease control. These results have increased awareness and enhanced biosecurity practices in areas of wildlife trade and livestock husbandry.
In five provinces, the second component of food safety comprises pilot interventions at 16 slaughterhouses and 68 retail points. It was intended to decrease the contamination of pork with Salmonella. These initiatives improved product safety and enhanced the sustainability of value chains.
In order to address the increasing challenge of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in poultry, the third component of the problem was addressed through the implementation of prudent antibiotic use and improved surveillance in Thai Nguyen Province.
The significance of an integrated approach and the effectiveness of collaboration are illustrated by these accomplishments, according to Dr. Unger. In spite of this, he acknowledged that additional effort is required to expand and maintain the initiative's effects.
The ILRI affirmed its dedication to advancing Vietnam's One Health objectives, with the expectation that ongoing interdisciplinary collaboration will guarantee a healthier future for all.
For Component 1, regarding the evaluation of wildlife value chains and the risk of zoonotic disease transmission, the project leaders emphasized that zoonotic disease transmission remains a significant concern. Increasing human-wildlife interactions and the expansion of wildlife value chains exacerbate this issue.
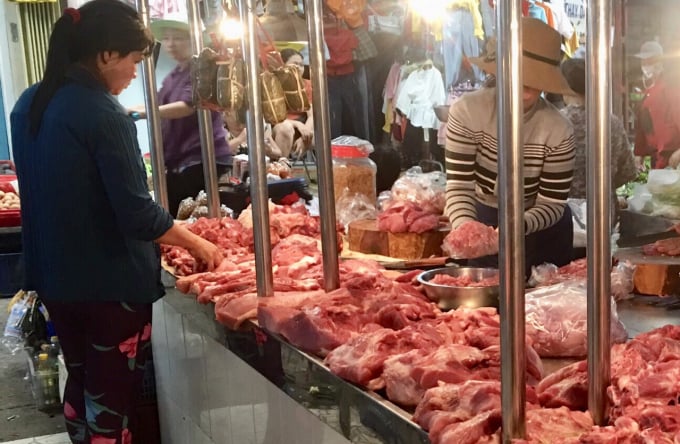

Microbial contamination at meat counters, especially Salmonella contamination, is a concern when contamination levels are high.
Laboratory tests confirmed that individuals engaged in wildlife husbandry had previously been exposed to pathogens, underscoring the genuine danger of zoonotic diseases. The knowledge and awareness of cultivators and consumers regarding zoonotic diseases and preventive measures, however, are still limited. Some individuals maintain a dismissive attitude, as they do not believe in the risks of zoonotic transmission, which exacerbates the risks to the health of both individuals and communities. This highlights the pressing necessity of implementing safety measures and increasing awareness in wildlife-related activities.
In the context of food safety, the experimental results indicated that meat stalls were plagued by persistent microbiological contamination, with Salmonella contamination rates being particularly high across all pilot sites. Contamination levels decreased in central and southern regions, while they increased in northern regions, potentially as a result of environmental and temperature factors. Intervention measures demonstrated varying impacts across regions. It is important to note that the impact of enhanced hygiene measures was demonstrated by the substantial reduction in contamination levels at markets where interventions were implemented.
In terms of vendors' knowledge, awareness, and practices, the provision of equipment and training programs substantially enhanced their awareness of hygiene and food safety. Compared to their previous practices, vendors who were provided with instruments exhibited significant improvements in their hygiene practices. As they observed the growing consumer concern regarding food quality and safety, their awareness was heightened. Subsequently, vendors in the intervention group implemented hygiene methods more frequently. In intervention markets, this achieved not only an increase in average revenue of 10%, but also an improvement in hygiene.
Representatives of the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) observed that 79% of antibiotics were employed in poultry husbandry for treatment purposes, while 19% were used for preventive purposes, as indicated by pilot studies on antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Overall, there were numerous similarities in the way small and medium-scale farmers perceived the advantages of antibiotics. However, there were gaps in their recognition of the drawbacks or issues associated with antibiotic use.
The cost of antibiotic use per production cycle was considerably higher for medium-scale households, with an average of 7.4 million VND, than for small-scale households, which had an average of only 1.4 million VND. This is to be noted. In an effort to guarantee economic efficiency and protect public health, these figures underscore the necessity of more rigorous antibiotic management practices, such as the prevention of misuse and the maintenance of detailed records.
Translated by Dieu Linh

(VAN) Agriculture and environment sector experienced a 3.74% increase in growth during the first four months of 2025, with exports surpassing 21 billion USD. This growth was sustained by effective reforms and a trade surplus.

(VAN) Taiwan offers a promising market for Vietnamese turmeric; however, it enforces stringent standards, particularly concerning residual additives, colourants, and substances with potential carcinogenic effects.

(VAN) Through activities at Vietnam Sea and Island Week 2025, solutions will be developed to fully harness the potential and advantages of Vietnam's marine economy.
![Multi-channel, multi-directional Vietnamese agricultural markets: [4] EVFTA and the 0% tax advantage](https://t.ex-cdn.com/nongnghiepmoitruong.vn/608w/files/linhnhp/2025/05/12/day-chuyen-che-bien-tom-tai-1-nha-may-cua-sao-ta-205536_359-1044193.jpg)
(VAN) The near-complete elimination of import tariffs on Vietnamese goods makes the EVFTA the highest commitment the EU has ever made to a partner in its signed trade agreements.

(VAN) Deputy Minister Phung Duc Tien hopes that China will facilitate the entry of Vietnamese agricultural products into its market and accelerate customs clearance at border gates.

(VAN) On May 10, the Animals Asia Foundation and the Hai Phong Crop Production and Forest Protection Department successfully rescued a nearly 20-year-old sun bear that was being kept by locals.
(VAN) Does Hungary have an opportunity to expand poultry production in the coming years despite the pressure from avian influenza and challenges of the trade war?