May 14, 2025 | 08:58 GMT +7
May 14, 2025 | 08:58 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
May 14, 2025 | 08:58 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
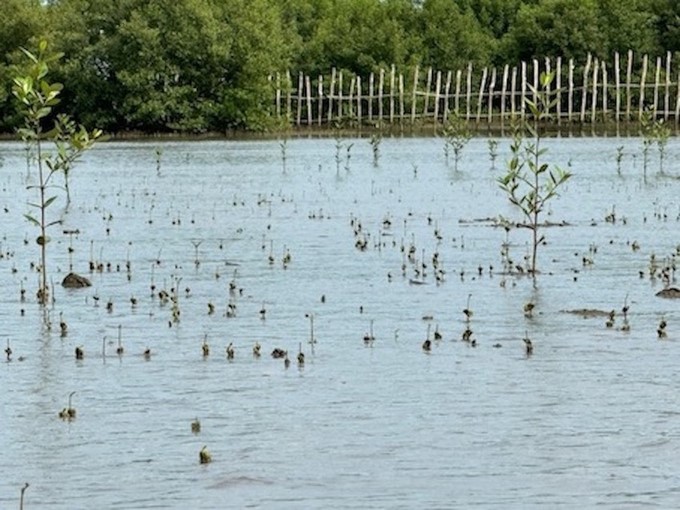
Inside the fence protecting 25 hectares of forest, more than 71,000 baby mangrove trees have grown to 40–50 cm tall, becoming a breeding ground for fish and shrimp and attracting flocks of coots, swallows, etc. to return to nest.
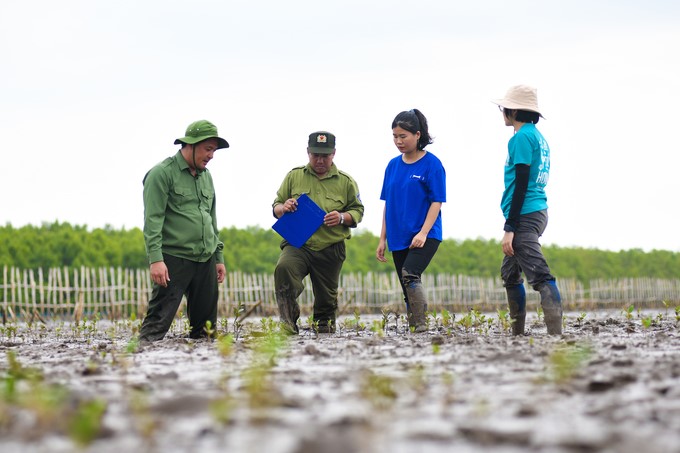

The Net Zero Vinamilk Forest in Mui Ca Mau National Park has miraculously regenerated.
Located deep in the core area of Mui Ca Mau National Park, Net Zero Vinamilk Forest has been implemented by Vinamilk, along with the Gaia Nature Conservation Center and Mui Ca Mau National Park, to nurture and promote regeneration since August 2023. The project has an area of 25 hectares, with the goal of regenerating 100,000–250,000 trees in 6 years (2023–2029).
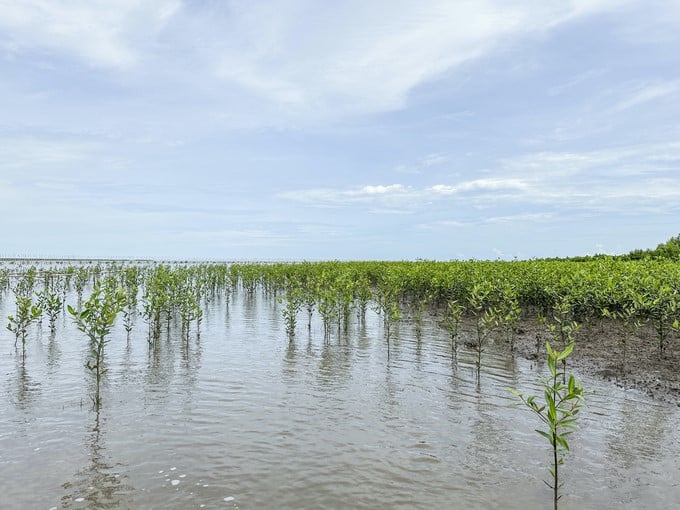

In less than 9 months since the fence was erected, the forest has welcomed more than 71,000 first-time "residents."
In less than 9 months since the fence was erected, the forest has welcomed more than 71,000 first-time "residents." These are black mangrove trees that sprouted from the seeds of "mother" mangrove trees that fell last August. With a unique lung root system that grows bottom-up, mangrove trees are likened to brave "soldiers," helping to stabilize mud and creating conditions for other plants such as Aegiceras corniculatum, Bruguiera, etc. to encroach towards the sea. Each year, the alluvial land can encroach nearly 100 m into the sea.
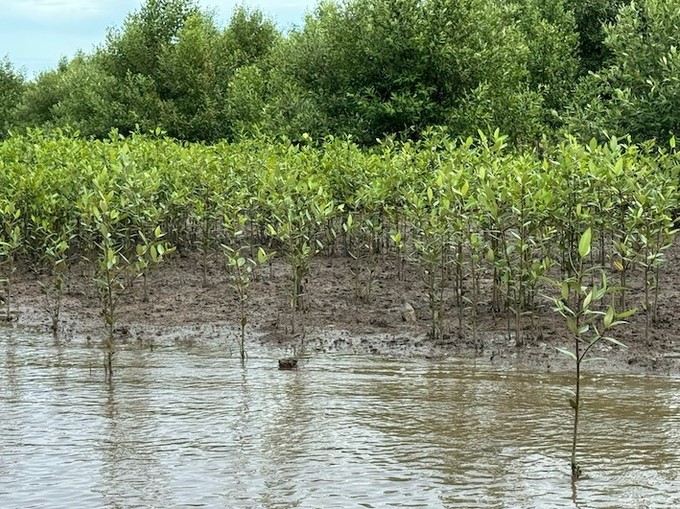

25 hectares of forest regenerated in cooperation with Vinamilk will soon be greened, faster than the initially set goal.
Up to this point, more than 71,000 baby mangrove trees have grown to 40–50 cm tall. Mr. Nguyen Van Su, Head of the Department of Science Technology and International Cooperation at Mui Ca Mau National Park, said that the density of regenerated mangrove trees in Net Zero Vinamilk Forest is quite thick. "With the current rate of development, we believe that the 25 hectares of forest regenerated in cooperation with Vinamilk will soon be greened, faster than the initially set goal," he said.

The Net Zero Vinamilk Forest area is bustling thanks to flocks of swallows, coots, etc., with hundreds of heads flying around.
Going by boat from afar, it is easy to recognize the Net Zero Vinamilk Forest area thanks to flocks of swallows, coots, etc., with hundreds of heads flying around, bustling the whole area. According to her many years of experience in nurturing mangrove forests, Ms. Huyen Do, Founder and Director of Gaia Nature Conservation Center, said that this is a very happy sign. Because flocks of birds and storks show that the vegetation and forest biota are developing well.
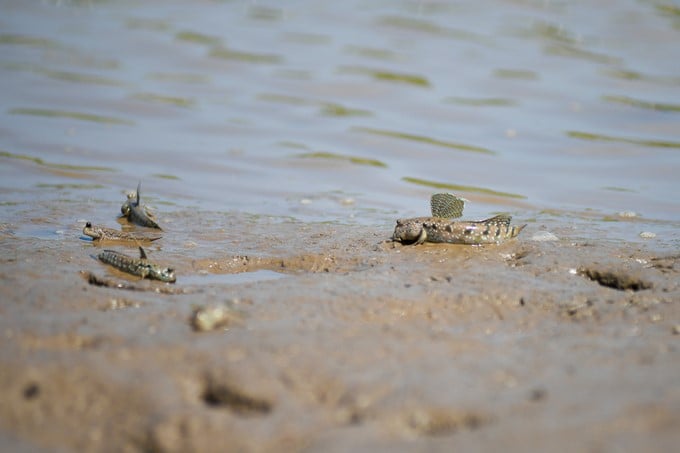

Many species of fish and seafood have come to Net Zero Vinamilk Forest to reproduce.
Thanks to being protected, countless species of fish and seafood have come to Net Zero Vinamilk Forest to reproduce. Swiftly moving on the alluvial ground are giant mudskippers, Boddart's goggle-eyed gobies, sesarmid crabs, snails, etc., looking for food.

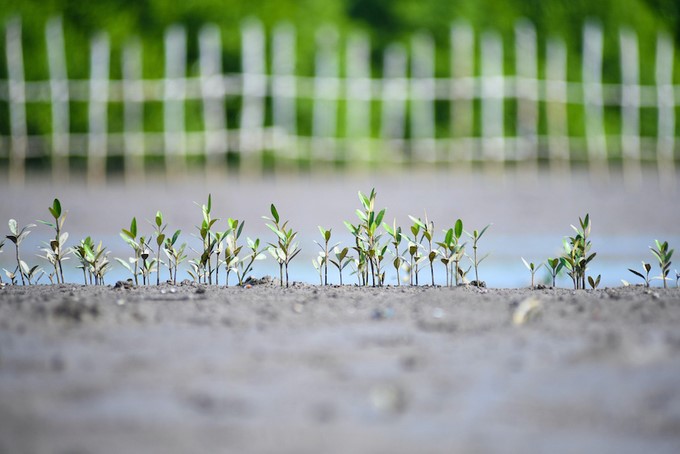
Around the tall mangrove trees, there are countless white mangrove seeds that are sprouting.
The special thing is that around the tall mangrove trees, there are countless white mangrove seeds that are sprouting. According to Ms. Huyen Do, Founder and CEO of Gaia, this is quite strange when the season of mangrove trees shedding seeds and regenerating in Mui Ca Mau National Park is usually around August–October every year.

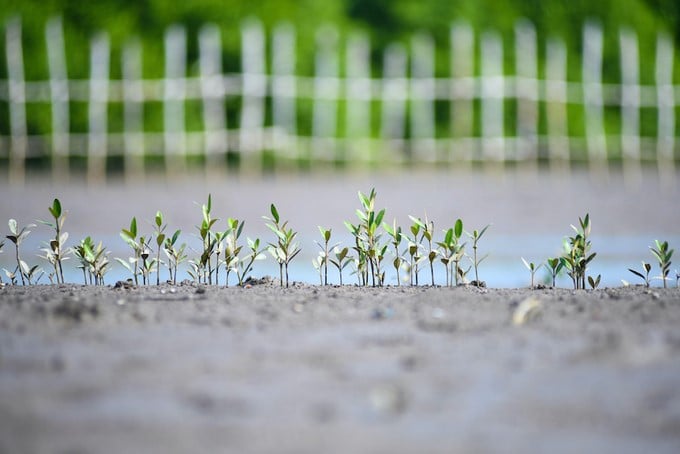
The white mangrove seeds that fell around last May have stayed and sprouted.
"This is a very good sign when the white mangrove seeds that fell around last May have stayed and sprouted. For many years of promoting mangrove forest regeneration, we have rarely seen so many mangrove seeds sprouting in May," said Ms. Huyen.

A lot of fish seeds sprout in the Net Zero Vinamilk Forest area.
The area that is currently empty land will gradually be filled with the green of mangrove trees in the next few years, contributing to the expansion of mangrove forests, sea encroachment, and land preservation.
Every year, Vinamilk, Gaia, and Mui Ca Mau National Park will jointly implement works such as reinforcing fences, closely monitoring tree growth, and preventing risks such as diseases and adverse weather to ensure forest regeneration achieves the set goal after 6 years.

Net Zero Vinamilk Forest is deployed with the goal of building a 'sink' with a capacity of 17,000–20,000 tons of carbon.
With the ability to absorb carbon 4–10 times more effectively than terrestrial forests, Net Zero Vinamilk Forest is deployed with the goal of building a "sink" with a capacity of 17,000–20,000 tons of carbon, equivalent to 62,000–73,000 tons of CO2e. This is one of Vinamilk's specific actions towards the goal of achieving Net Zero by 2050.

Net Zero Vinamilk Forest is deployed with the goal of building a 'sink' with a capacity of 17,000–20,000 tons of carbon.
Translated by Thu Huyen

(VAN) Deputy Minister of Agriculture and Environment Hoang Trung affirmed that floriculture and ornamental plants are a growing industry that receives significant global attention.

(VAN) The three staple crops dominating modern diets – corn, rice and wheat – are familiar to Americans. However, fourth place is held by a dark horse: cassava.
/2025/05/10/4037-3-223011_495.jpg)
(VAN) Remote sensing technology is becoming an indispensable tool in monitoring resources, developing modern agriculture, and protecting the environment in Vietnam.

(VAN) The trash bag used on fishing vessels can withstand rough sea conditions, including level 8 to level 10 winds and waves. Notably, it can be hung anywhere on the boat.

(VAN) African leaders launched the Kampala Declaration on Building Resilient and Sustainable Agrifood Systems in Africa, marking a bold step toward transforming the continent's agriculture.
(VAN) Can Tho City Department of Agriculture and Environment demands administrative sanctions on households that do not comply with vaccinating their livestock as a deterrent.

(VAN) With a strict veterinary process and close production chains, Dong Thap ensures that pangasius is disease-free from farm to table.