June 25, 2025 | 22:56 GMT +7
June 25, 2025 | 22:56 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
June 25, 2025 | 22:56 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
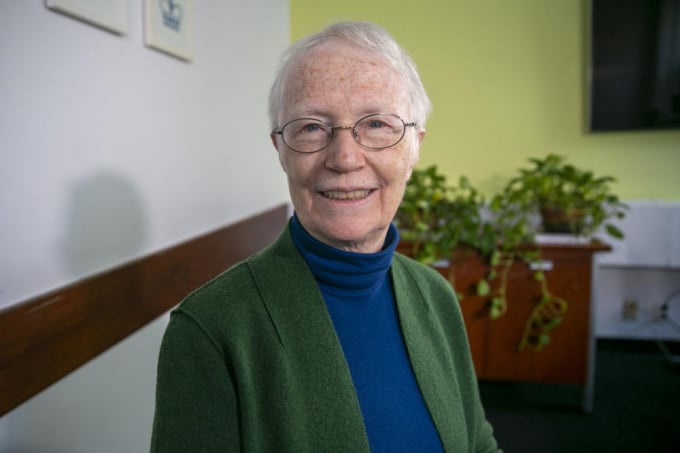

Cynthia Rosenzweig, 2022 World Food Prize recipient, meets with the media at the Columbia University Climate School in New York City on Tuesday, May 3, 2022. Rosenzweig is a senior research scientist and head of the Climate Impacts Group at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, the Goddard Institute for Space Studies and the Columbia University Climate School. She won the prize because of her work modeling the impact of climate change on food production. Photo: AP
Cynthia Rosenzweig, an agronomist and climatologist, was awarded the $250,000 prize in recognition of her innovative modeling of the impact of climate change on food production. She is a senior research scientist at the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies and serves as adjunct senior research scientist at the Columbia Climate School at Columbia University, both based in New York.
Rosenzweig, whose win was announced during a ceremony at the State Department in Washington, said she hopes it will focus attention on the need to improve food and agricultural systems to lessen the effects of climate change.
“We basically cannot solve climate change unless we address the issues of the greenhouse gas emissions from the food system, and we cannot provide food security for all unless we work really hard to develop resilient systems,” she told The Associated Press during an interview ahead of the ceremony.
Jose Fernandez, the undersecretary of state for economic growth, energy and the environment, said more than 160 million people worldwide experienced food insecurity last year, a 19% increase over the year before, and one of the root causes is a decline in food production due to global warming.
“Climate change has already had a significant and negative impact on global agricultural production and its impact is only going to get worse. We’re seeing rice fields drown in floods. We’re seeing other crops wither in drought. We’re seeing shellfish die in more acidic oceans and crop diseases are spreading to new regions. We likely would not understand all these problems as well as we do today without the work of Dr. Cynthia Rosenzweig, this year’s World Food Prize laureate,” he said.
The Des Moines-based World Food Prize Foundation award recognized Rosenzweig as the founder of the Agricultural Model Intercomparison and Improvement Project. The organization draws scientists from around the world and from many disciplines to advance methods for improving predictions of the future performance of agricultural and food systems as the global climate changes.
The foundation credited her work with directly helping decision-makers in more than 90 countries establish plans to prepare for climate change.
In her work, Rosenzweig has studied how farmers can deal with climate change and how agriculture worsens the problem. For example, she contributed to a research paper published last month that said global agri-food systems create nearly one-third of the total global greenhouse gases emitted by human activity.
Rosenzweig said the world needs to reduce such emissions and adapt to the changing climate. She noted that greenhouse gases come from many parts of food production, including the release of carbon and carbon dioxide through the clearing of forests for farmland and the oxidization of carbon through the plowing of fields. The use of fertilizer also releases atmospheric nitrous oxide, farm equipment emits fossil fuels and cattle release methane.
Rosenzweig, who describes herself as a climate impact scientist, grew up in Scarsdale, New York, a suburban area that she said led her to seek out life in the country. She moved to Tuscany, Italy, with her husband-to-be in her 20s and developed a passion for agriculture. Upon returning to the United States, she focused her education on agronomy.
She worked as a graduate student at the Goddard Institute for Space Studies in the early 1980s, when global climate models were beginning to show the effects of human generated carbon dioxide on the global climate. As the only team member studying agronomy, she researched the impact on food production and has been working since then to answer those questions, she said.
Rosenzweig’s work led to the Environmental Protection Agency’s first projections of the effect of climate change on the nation’s agricultural regions in the agency’s assessment of the potential effects of climate change on the United States in 1988. She was the first to bring climate change to the attention of the American Society of Agronomy and she organized the first sessions on the issue in the 1980s.
She completed the first projections of how climate change will affect food production in North America in 1985 and globally in 1994, and she was one of the first scientists to document that climate change was already impacting food production and cultivation.
The research organization she founded, AgMIP, develops adaptation packages, which could include the use of more drought-tolerant seeds and improved water management practices. In Bangladesh the group is working with rice farmers to develop new practices for managing rice paddies to reduce the significant release of methane produced by the existing process.
She said even the largest agribusiness corporations have shown a willingness to listen. She said some models colleagues have developed show how businesses could be effected by climate change and how they too have a role to play in reversing impact on climate.
“It’s really a global partnership of all the global food system to come together to restrain climate change and maintain the food security for the planet,” she said.
World Food Prize Foundation President Barbara Stinson, who announced the winner, credited Rosenzweig for innovations that helped countries respond to climate change.
Nobel Prize laureate Norman Borlaug created the World Food Prize in 1986 to recognize scientists and others who have improved the quality and availability of food. Rosenzweig will receive the award and make a speech during an October ceremony in Des Moines.
(AP)

(VAN) In the suburbs of Beijing, there is an agricultural center spanning over 150 hectares dedicated to research, demonstration, and application of high-tech and precision agriculture.
(VAN) Researchers from the Institute of Applied Ecology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a new environmentally friendly fertilizer additive that significantly enhances crop yields while reducing emissions of harmful gases.

(VAN) Poultry production in Poland, which has only started recovering from devastating bird flu outbreaks earlier this year, has been hit by a series of outbreaks of Newcastle disease, with the veterinary situation deteriorating rapidly.

(VAN) Extensive licensing requirements raise concerns about intellectual property theft.

(VAN) As of Friday, a salmonella outbreak linked to a California egg producer had sickened at least 79 people. Of the infected people, 21 hospitalizations were reported, U.S. health officials said.

(VAN) With the war ongoing, many Ukrainian farmers and rural farming families face limited access to their land due to mines and lack the financial resources to purchase needed agricultural inputs.

(VAN) Vikas Rambal has quietly built a $5 billion business empire in manufacturing, property and solar, and catapulted onto the Rich List.