April 22, 2025 | 02:35 GMT +7
April 22, 2025 | 02:35 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
April 22, 2025 | 02:35 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918

Photo: Sarah Darmanjian
Supply shortages are causing the price of food to go up, this is likely to continue into 2022 based on market research from the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA).
An increase in food prices, especially for meat and dairy products, may have put the squeeze on household budgets during 2020 when year over year prices rose anywhere between 2.2% and 9.6% depending on the food, the USDA said in its most recent Food Price Outlook. Although the price of food hasn’t recently spiked as it did in early 2020, the USDA said they don’t expect prices to come down through 2022 from where they are currently.
Food prices in 2020 and the first half of 2021
Beef, pork, and chicken had the most significant change in 2020. Beef and veal jumped 9.6%, the highest percentage. Pork came in second with a 6.3% increase and chicken third with a 5.6% increase. The price index for fresh fruit actually went down in 2020 (-.8%), but that didn’t hold with an increase of 7.3% year-to-date (YTD) average in 2021.
USDA change in food price indexes
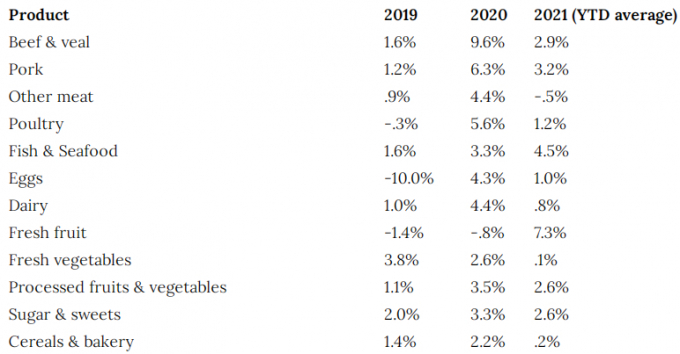
Source: USDA
Looking at data from the USDA, notable spikes in the price of meat and eggs can be seen in early to middle 2020, with fewer dramatic fluctuations in the price of tomatoes and white bread. Year over year, from June 2020 to June 2021 the average price of all four foods has gone down.
Between January 2020 and June 2021, the cost of meat spiked to its highest price in June 2020. The average price for a pound of beef in January 2020 was $4.10, by June it was $5.33. The price of eggs spiked in April. A dozen large eggs cost an average of $1.46 in January, in April it was $2.02.
Looking ahead
The USDA said the price of food bought from a grocery store will increase anywhere from 3.5% to 5.5% in 2021 and 2022. Using the June 2021 price for a pound of beef ($4.57), a 3.5% increase would drive the cost up $.16 to $4.73 and a 5.5% increase would drive the cost up $.25 to $4.82.
For a large dozen of eggs, a 3.5% increase would add $.06 and a 5.5% increase would add $.09 to the June 2021 price of $1.64. A pound of tomatoes would also go up about $.06 with a 3.5% increase and a $.10 with a 5.5% increase.
What would this mean in terms of overall cost? Someone who spends $125 a week at the grocery store would spend an additional $4.38 with a 3.5% increase and an additional $6.88 with a 5.5% increase. Someone who spends $200 would spend between an additional $7 (3.5%) or $11 (5.5%).
As far as restaurants or eateries, the USDA said they expect those prices to increase more than prices in grocery stores, between 6% and 8% by 2022. On the lower end, it would add $3.60, and on the higher end it would add $4.80 to a $60 bill.
(News10.com)

(VAN) Warmer temperatures and more carbon dioxide will boost levels of arsenic, a dangerous heavy metal, according to new research.

(VAN) California's $59 billion agriculture industry faces serious disruption as the U.S. clashes with China - one of the state's major export markets.

(VAN) Five things you should know about Sudan's food security crisis.

(VAN) 169 lotus seeds selected by the Vietnam Academy of Agricultural Sciences were carried into space by Vietnamese-American astronaut Amanda Nguyen.

(VAN) Tariffs are making life more expensive for John Pihl. He's been farming in Northern Illinois for more than 50 years.

(VAN) European and American farmer organisations are concerned about the import tariffs that the United States introduced on 9 April for products from the European Union. This makes them 20% more expensive.

(VAN) Global poultry trade is expected to remain strong amid relatively tight global protein supply and growing consumption, RaboResearch concludes in its latest animal protein report.