May 21, 2025 | 02:05 GMT +7
May 21, 2025 | 02:05 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
May 21, 2025 | 02:05 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918

The year-on-year leap in UN Food and Agriculture Organization’s monthly food price index was the largest since 2011 and signalled that inflation initially stoked by pandemic disruption is accelerating.
China’s soaring appetite for grain and soyabeans is adding to upward pressure on prices, along with a severe drought in Brazil and growing demand for vegetable oil for biodiesel.
The index is a key benchmark for internationally traded agricultural commodities and the increase brings it to its highest level since September 2011.
The rise in world market prices will further increase food price inflation especially among poorer countries reliant on imports for staples.
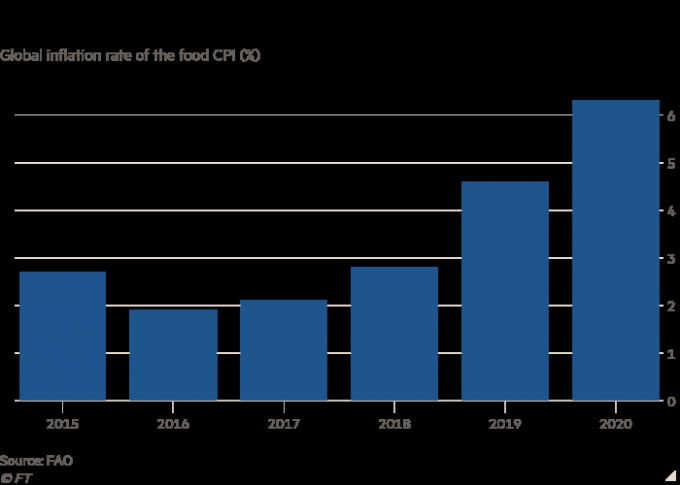
In 2020, the world’s consumer price inflation for food jumped to 6.3 per cent, up from 4.6 per cent in 2019, according to the FAO.
The pandemic disrupted food supply chains, affecting the production and distribution of food, with South Asia, sub-Saharan Africa and Latin America among the most affected regions.
The bad weather in Brazil, a big exporter of corn and soyabeans, and rising demand for soyabean oil for biodiesel have pushed prices higher, said analysts.
“China has continued to buy, but with Brazil’s drought proving to be more severe than expected, everyone has to pray that the weather in the US is going to be good,” said Abdolreza Abbassian, senior economist at the FAO.
Countries that depend on overseas producers for their staples have been hit by higher global food prices. The issue has become a political concern in some developing countries such as Ethiopia and Nigeria.
Some exporting countries have introduced an export tariff, such as Russia for its wheat sales, while others such as Argentina are discussing a controversial ban on beef exports.
In developed countries, the cost of raw ingredients accounts for only part of the overall price paid for products at the supermarket or in restaurants.
But the surge in commodity prices is leading to higher food prices, with companies such as Nestlé and Coca-Cola announcing they will pass on the price increases.
The opening of restaurants as lockdowns ease will add to the food bill, said Abbassian. “The decline in eating out wasn’t totally compensated with eating at home, but as people start to go to restaurants again, you will see food prices rise,” he said.
(Finacial Times)

(VAN) In 2024, over 295 million people across 53 countries and territories faced acute hunger—an increase of almost 14 million people compared to 2023, while the number of people facing catastrophic levels of hunger reached a record high.

(VAN) World Environment Day 2025 (June 5) carries the theme 'Beat Plastic Pollution' continuing to emphasize the global urgency of addressing the plastic waste crisis.

(VAN) This was the assessment shared by experts at the workshop titled 'Assessing the Role and Potential of Low-Emission Rice Production Systems in Vietnam,' held on the morning of May 19.

(VAN) Cai Rong Port is the fisheries control center of Quang Ninh, helping to monitor fishing vessels, combat IUU fishing, and remove the EC's 'yellow card'.

(VAN) The German Agricultural Society (DLG) explores the possibility of establishing a mechanization service center in Vietnam’s Mekong Delta to support farmers in accessing and utilizing advanced machinery.

(VAN) On May 16, the Department of Water Resources Management, in collaboration with the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), held a signing ceremony for the GEF-8 project document.

(VAN) Food safety, mechanization, vocational training, and market opening are key areas of cooperation expected between the Vietnamese Government and the Federal Republic of Germany.