June 19, 2025 | 08:55 GMT +7
June 19, 2025 | 08:55 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
June 19, 2025 | 08:55 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918

Every fruit or vegetable on the list contains two or more types of pesticide, with some containing up to 25. Photo: Imaginechina Limited/Alamy
Almost all grapes and oranges contain a “cocktail of pesticides” according to research, which has singled out the most polluted fruit and vegetables in our shopping trolleys.
Each year, the government tests samples of groceries for chemicals to see if traces can be found in Britain’s food.
The official figures, analysed by Pesticide Action Network (PAN), found 122 different pesticides in the 12 most polluted products, which the charity calls the “dirty dozen”. Many of these are hazardous to human health; 61% are classified as highly hazardous pesticides (HHPs), a concept used by the UN to identify those substances most harmful to human health or the environment.
The list of pesticides includes 47 with links to cancer, 15 “reproductive or developmental toxins” that can have adverse effects on sexual function and fertility, and 17 cholinesterase inhibitors that can impair the respiratory system and cause confusion, headaches and weakness. A quarter of the pesticides found are suspected endocrine disruptors that can interfere with hormone systems, causing an array of health problems including birth defects and developmental disorders.
Every fruit or vegetable on the list contains two or more types of pesticide, with some containing up to 25. Although the levels of individual pesticides are within legal limits, activists fear the combination of multiple chemicals could be particularly damaging to people’s health.
Nick Mole from PAN UK said: “These figures highlight the wide array of chemicals that we are exposed to daily through our diets. While safety limits continue to be set for just one pesticide at a time, the evidence is growing that chemicals can combine to be more toxic, a phenomenon known as the cocktail effect.”
There are also gaps in the data. This year the government chose to test only three of the 12 types of fruit and vegetables from last year’s dirty dozen list compiled by PAN. Strawberries, lemons and pre-packed salad, which topped the previous list, were not tested so there is no way of knowing if the amount of pesticides on these products was reduced.
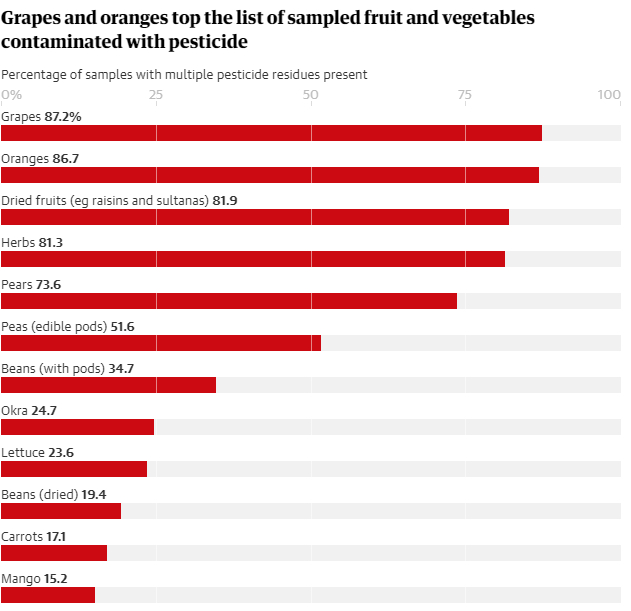
Guardian graphic | Source: Data presented based on PAN UK analysis of the UK Government’s Expert Committee on Pesticide Residues in Food (PRiF) Annual Report 2020
A spokesperson for PAN said there was no real way to avoid ingesting pesticides, other than campaigning for a reduction in their use.
“The best way for people to avoid pesticides is to buy organic. Of course, almost no one in the UK can financially afford or access a fully organic diet so that is why we publish the dirty dozen – to help consumers prioritise which produce to avoid,” she said.
“In terms of washing, it should remove some residues on the skin of a product (which will often be fungicides used to prevent rotting during storage and transportation). However, many modern pesticides are what are called ‘systemic’ which means that they are absorbed into the plant and distributed throughout its tissues, reaching any fruits or flowers. As a result, pesticide residues are often contained within the body of the produce itself and therefore washing the surface won’t remove them.”
It is also recommended that consumers buy from EU countries as well as the UK, as the EU has by far the most protective pesticide regime in the world and is far more likely to ban a pesticide due to concerns over the harms it causes. The UK regime currently mirrors the EU regime.
There are also environmental implications: half of the top 12 pesticides found are groundwater contaminants, meaning they persist in water bodies, potentially affecting aquatic biodiversity or drinking water quality. The list includes the neonicotinoid acetamiprid which, while thought to be less toxic to pollinators than other neonicotinoids, PAN says could still represent a potential threat to bee health.
Mole added: “Consumers presume that their food has been through rigorous testing and that if an item is available for sale in the UK then it must be safe. Unfortunately, this is not necessarily the case. We actually have very limited understanding of the long-term impacts to human health of consuming small amounts of tens of different pesticides every day of our lives.”
A spokesperson for the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs said: “All food sold in the UK must meet strict rules on pesticide residue to ensure it is safe to eat. These are enforced via a comprehensive residues monitoring programme overseen by an independent specialist body and in 2020 more than 97% of tested samples were compliant.
“However we continue to encourage a move away from chemical pest control, and recently consulted on a national action plan which aims to minimise the impacts of pesticides and increase the uptake of safer alternatives.”
(Guardian)

(VAN) Extensive licensing requirements raise concerns about intellectual property theft.

(VAN) As of Friday, a salmonella outbreak linked to a California egg producer had sickened at least 79 people. Of the infected people, 21 hospitalizations were reported, U.S. health officials said.

(VAN) With the war ongoing, many Ukrainian farmers and rural farming families face limited access to their land due to mines and lack the financial resources to purchase needed agricultural inputs.

(VAN) Vikas Rambal has quietly built a $5 billion business empire in manufacturing, property and solar, and catapulted onto the Rich List.

(VAN) Available cropland now at less than five percent, according to latest geospatial assessment from FAO and UNOSAT.

(VAN) Alt Carbon has raised $12 million in a seed round as it plans to scale its carbon dioxide removal work in the South Asian nation.

(VAN) Attempts to bring down the price of the Japanese staple have had little effect amid a cost-of-living crisis.