May 27, 2025 | 05:23 GMT +7
May 27, 2025 | 05:23 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
May 27, 2025 | 05:23 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918

Workshop on “Opportunities and technical solutions for high-quality, low-emission rice production in the Mekong Delta” on October 8. Photo: Quynh Chi.
The workshop provided an overview of research on climate-resilient rice varieties, sustainable farming methods, and emission reduction strategies aligned with global trends. Additionally, scientists from the International Rice Research Institute presented its support in developing a MRV (measurement, reporting, and verification) system, along with capacity building for localities involved in the “1 million hectares of high-quality, low-emission rice linked to green growth in the Mekong Delta by 2030” project (the Project).
“The primary goal of the Project is to reorganize production by establishing specialized rice cultivation zones and implementing sustainable farming practices to adapt to climate change. We aim to standardize emission reduction processes, and certified carbon credits will serve as a key indicator of successful sustainable rice farming,” said Director Nguyen Do Anh Tuan.
To date, the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development has finalized the Technical Process for High-Quality, Low-Emission Rice Production in the Mekong Delta, as well as a Capacity Building Plan for Partners and Agricultural Cooperatives to develop value chain linkages for Project implementation. During the upcoming winter-spring and summer-autumn crops, the Ministry will oversee the expansion of pilot areas, working towards measuring the carbon emission coefficient of rice plants.

Dr. Nguyen Do Anh Tuan: “Carbon credits are a benchmark of the success of sustainable rice cultivation.” Photo: Quynh Chi.
To enhance the existing irrigation infrastructure and complete the integrated canal and transportation system, the Ministry has assessed the current infrastructure in rice production zones participating in the Project. The Ministry has also gathered the needs proposed by the provinces and is actively seeking resources to invest in upgrading these specialized zones.
Based on the Ministry’s assessments and discussions with the 12 localities involved in the Project, achieving the 2030 targets will require approximately USD 3 billion. Enterprises and farmer organizations are expected to contribute 60% of the total capital, with the remaining 40% coming from preferential loans.
“For the Project, the largest bottleneck lies in infrastructure investment. Therefore, the International Cooperation Department is advocating for a special mechanism for foreign loans,” noted Dr. Tuan.
Lack of mechanisms to encourage farmers to produce low-emission rice
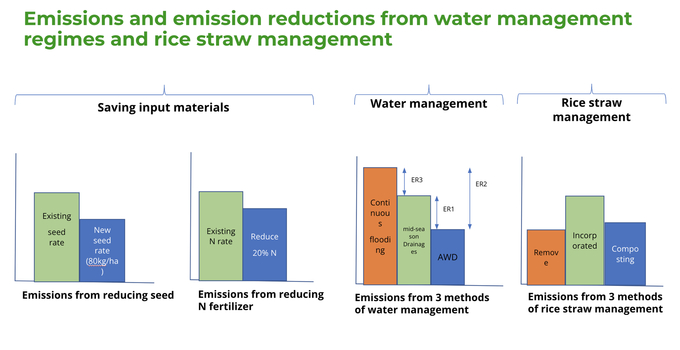
According to the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), low-emission rice production technologies can reduce methane emissions by about 65%. Specifically, improved water management techniques, such as alternate wetting and drying (AWD), can reduce methane emissions by an average of 33%. Additionally, eliminating straw burning can cut emissions by up to 15%, while burying straw combined with AWD can reduce emissions by 10%. Short-season rice varieties also contribute by lowering greenhouse gas emissions by 7%.
However, Le Thanh Tung, Deputy Director of the Department of Crop Production, noted that one of the main obstacles to reducing emissions in rice farming is that local authorities are primarily focused on economic growth and food security goals. As a result, emission reduction efforts have not been given the necessary attention.
There is still a lack of mechanisms to encourage farmers to produce low-emission rice. Photo: Le Thanh Tung.
Mr. Tung remarked, “Prioritizing yield and immediate income has hindered the adoption of environmentally friendly practices in the production process.”
In addition, there is a significant lack of specific mechanisms to incentivize farmers to shift toward low-emission rice production. Without clear and concrete benefits, farmers often see little reason to abandon their traditional, higher-emission farming methods, making it difficult to scale up emission reduction initiatives.
Moreover, many rice-producing regions still struggle with infrastructure deficiencies, particularly in irrigation systems, which are inadequate for implementing measures such as AWD. These infrastructure gaps make the adoption of new technologies inconsistent and challenging across different localities.
The costs associated with low-emission rice farming practices remain high, often beyond the financial capacity of many farmers. This further limits access to and the implementation of emission reduction measures, especially for smallholder farmers who may lack the resources to invest in such practices.
During the open discussion, former Deputy Minister of Agriculture and Rural Development, Dr. Bui Ba Bong, who is also the Chairman of the Vietnam Rice Industry Association (VIETRISA), pointed out that while farmers may not focus heavily on emission reduction, they are very conscious of sustainable production and fully capable of engaging in such practices.
The concept of “low emission” remains relatively new and difficult for producers to grasp, but the idea of “green” production is more readily accepted due to various incentives. Currently, VIETRISA is working to establish a sustainable rice brand, aiming to complete the registration for the trademark "Green and Low-Emission Vietnamese Rice" by the end of this month.

Dr. Bui Ba Bong: “VIETRISA is building a sustainable rice brand under the trademark green and low-emission Vietnamese rice.” Photo: Quynh Chi.
Can Tho is one of the first localities selected by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development to pilot a 50-hectare rice cultivation model aimed at reducing emissions. According to Pham Thi Minh Hieu, Director of the Can Tho's Department of Crop Production and Plant Protection, this is a significant challenge as the region has not previously implemented demonstration models on such a scale.
“Although farmers in the area were trained under the VnSAT project and had prior production experience, they were initially concerned about applying the new technique of using only 70 kg of seeds per hectare. However, after seeing the promising results, the farmers were enthusiastic about the initial success, paving the way for future expansion of the model,” noted Director Hieu.
Mechanization expert Phan Hieu Hien also shared valuable insights. He emphasized, “Scaling up the emission reduction farming model to 1 million hectares can only be achieved with the support of technological equipment, as biological and agronomic advancements must be complemented by technological infrastructure.”
Dr. Hien further stressed that the rice industry’s value chain is highly complex, yet current efforts are mostly focused on the production stages. He called for greater cooperation with the Ministry of Industry and Trade to support agricultural mechanization, a crucial area for improving production processes and enhancing the quality of the rice value chain.
At the event, the Department of Crop Production introduced scientific and technical advancements related to the "Technical solution of mechanized direct seeding combined with fertilizer burying in rice production in the Mekong Delta." This process ensures that rice plants receive adequate nutrition from the very first days after sowing. Moreover, direct seeding allows rice plants to come into direct contact with fertilizers, improving nutrient absorption, reducing fertilizer loss, promoting deeper root growth, and enhancing plant resistance to extreme climate conditions.
Translated by Quynh Chi

(VAN) The alignment in goals and operational direction between the Vietnam Agriculture and Nature Newspaper and Shaanxi Daily opens up promising prospects for journalism and media cooperation.
/2025/05/26/3422-3-102748_432.jpg)
(VAN) Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh has been honored as the Distinguished ASEAN Leader at the ASEAN Leadership and Partnership Forum (ALPF) 2025 held in Malaysia, affirming Vietnam’s role and reputation.

(VAN) At WHA78, with health placed at the heart of the global climate storm, Viet Nam enters a new commitment to protect communities from increasingly severe risks.

(VAN) Despite investment costs being 1.5 to 1.8 times higher than conventional methods, multi-story pig farming demonstrates outstanding effectiveness, increasing land-use efficiency by 4 to 10 times.

(VAN) Deputy Minister of Agriculture and Environment Phung Duc Tien leads a working delegation to participate in several key activities in China aimed at promoting agricultural and fisheries cooperation.

(VAN) The European Commission has just released a list of ‘low-risk’ countries for deforestation, which includes Vietnam.

(VAN) The convenience of single-use plastics is leaving lasting consequences for the oceans.