June 21, 2025 | 12:24 GMT +7
June 21, 2025 | 12:24 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
June 21, 2025 | 12:24 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
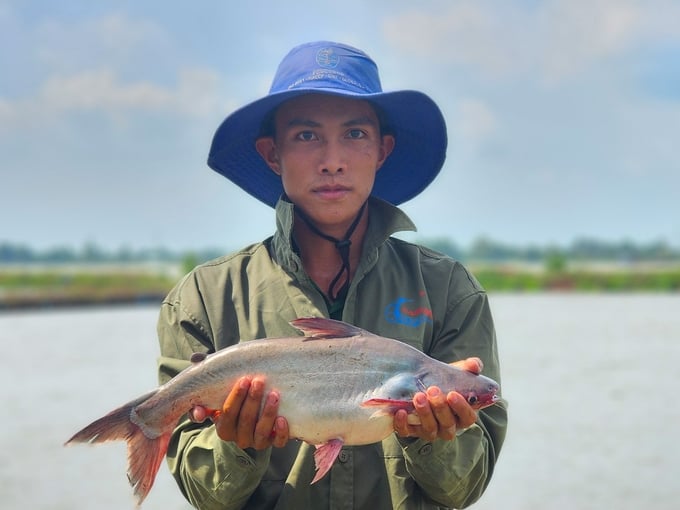

The shark catfish is a key aquaculture species in Vietnam, most commonly found in the Mekong Delta region, where it remained as a fast-growing export sector for multiple years. Photo: Kim Anh.
The production area and yield of shark catfish in Vietnam have fluctuated significantly in recent years, with disease outbreaks posing as one of the most critical challenges that increase farming costs.
According to experts from the College of Aquaculture and Fisheries at Can Tho University, Vietnam's control of infectious agents in aquaculture has relied primarily on the use of antibiotics.
However, strict management and control requirements for antibiotic residues in food products, in combination with the increasingly complex challenge of bacterial antibiotic resistance, highlights the implementation of aquatic animal health management practices as the optimal solution for disease prevention in shark catfish. This approach includes epidemiological methods, which aim to prevent disease outbreaks by adhering to the principle of "prevention over treatment."
Incomplete statistics from provinces in the Mekong Delta region revealed that over 435 hectares of shark catfish farming area were affected by disease outbreaks in 2023. This figure represents a significant decrease compared to previous years; however, disease outbreaks remain prevalent in provinces engaged in shark catfish farming.
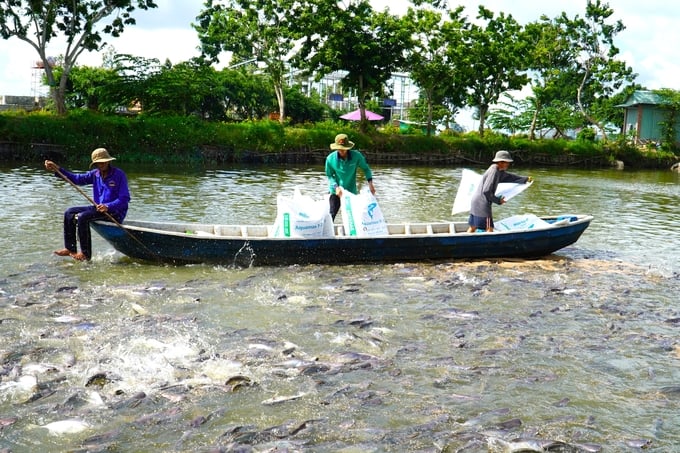

Effective disease control in shark catfish requires water quality management, supplementation of vitamins and minerals, immunostimulants, and vaccines. Photo: Van Vu.
Associate Professor Dr. Bui Thi Bich Hang from the Department of Aquatic Pathology at the College of Aquaculture and Fisheries reported that current common diseases in shark catfish include kidney-liver abscesses, hemorrhages, and tail rot.
Kidney-liver abscesses, which saw a significant increase during the flood season from July to September, now occur almost year-round.
Hemorrhages, another common disease in shark catfish, result in high mortality rates as high temperatures, or mechanical impacts during the harvesting and transportation process, cause stress to the fish. This disease often co-occurs with other conditions such as kidney-liver abscesses, jaundice syndrome, and swim bladder swelling disease.
Hemorrhages frequently occur multiple times throughout the farming cycle, significantly impacting fish growth, extending farming duration, and increasing treatment costs.
Tail rot disease is especially detrimental during the nursery stage, with mortality rates reaching 80 to 100% when exacerbated by fungal, bacterial, and parasitic infections.
Consequently, the key solutions to controlling disease outbreaks in shark catfish include water quality management, vitamin and mineral supplementation, and immunostimulant and vaccine usage.
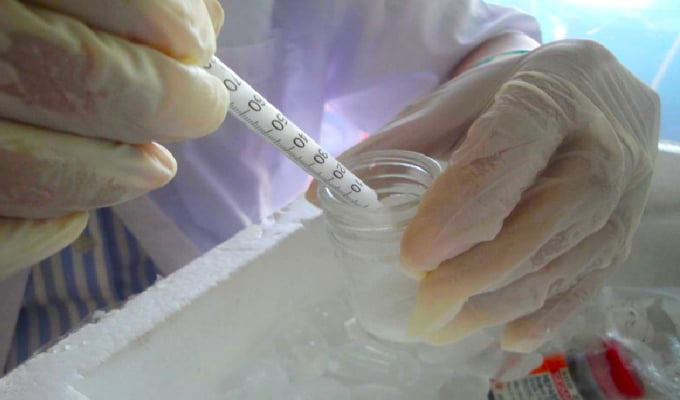
Shark catfish vaccinations are a promising solution to effectively protect against the adverse effects of diseases. Photo: College of Aquaculture and Fisheries.
Between 2020 and 2023, the College of Aquaculture and Fisheries implemented the Pangavacxin Project, with the aim of developing vaccines to prevent disease outbreaks in shark catfish. The project targets the development of vaccines to promote safety in disease prevention efforts, reduce antibiotic use, and decrease mortality rates in shark catfish in the Mekong Delta region.
Accordingly, experts collected samples and screened bacterial strains from commercial shark catfish ponds in Vietnam to prepare antigens. They developed three types of single and multivalent injectable vaccines, with plans to advance to oral and immersion vaccines for disease prevention in shark catfish. This initiative aims to promote the sustainable development of industrial shark catfish farming.
Results from the project indicate that the vaccines have protected shark catfish populations with relatively high efficacy rates, at between 90 and 100%, against pathogenic bacterial strains. This solution promises to provide effective protection for farmed shark catfish, improve the environment, and reduce pressures from trade barriers.
The revenue from shark catfish exports reached 918 million USD in the first six months of 2024, marking an increase of 5% compared to the corresponding period in 2023. Accordingly, shark catfish fillets stand as the most valuable export product with a total revenue of 739 million USD, marking an increase of 3%. Additionally, the revenue from fresh/frozen/dried pangasius exports reached 162 million USD, marking an increase of 17%. China and Hong Kong maintain their positions as the largest markets for Vietnamese shark catfish exports in the first six months with a total turnover of 258 million USD, marking a decrease of 8% compared to the corresponding period in 2023; followed by the US market at 160 million USD, an increase of 14%; CPTPP at 128 million USD, an increase of 11%.
Translated by Nguyen Hai Long
![Turning wind and rain into action: [9] Digitizing hydrometeorological data in response to climate change](https://t.ex-cdn.com/nongnghiepmoitruong.vn/608w/files/news/2025/06/17/z6704423696987_15fd32ffc26d590d204d520c9dac6786-nongnghiep-165943.jpg)
(VAN) Farmers have begun accessing hydrometeorological applications to adjust their cropping schedules, aiming to ensure productivity and adapt to climate change.
![Turning wind and rain into action: [8] Real-time salinity detection and early warning technology](https://t.ex-cdn.com/nongnghiepmoitruong.vn/608w/files/news/2025/06/17/z6704423696987_15fd32ffc26d590d204d520c9dac6786-nongnghiep-151127.jpg)
(VAN) Thanks to the integration of modern hydrological-hydraulic models, remote sensing technologies, and artificial intelligence, the accuracy of hydrological forecasting has significantly improved.
![Turning wind and rain into action: [7] Early disaster warnings help marine farmers minimize losses](https://t.ex-cdn.com/nongnghiepmoitruong.vn/608w/files/news/2025/06/17/z6704423696987_15fd32ffc26d590d204d520c9dac6786-nongnghiep-142942.jpg)
(VAN) In recent years, thanks to early disaster warnings and forecasting, marine farmers in Khanh Hoa province have been able to reduce risks and losses, thereby improving production efficiency.
![Turning wind and rain into action: [6] ‘Four on-the-spot’ disaster management software](https://t.ex-cdn.com/nongnghiepmoitruong.vn/608w/files/news/2025/06/17/e5a48259d6a262fc3bb3-nongnghiep-183800.jpg)
(VAN) By simply activating the scenario on the disaster management software, the relevant authorities immediately know how many households need to be evacuated, where to evacuate them to, and by what means of transportation…
![Turning wind and rain into action: [5] Hue applies modern technology in disaster forecasting](https://t.ex-cdn.com/nongnghiepmoitruong.vn/608w/files/news/2025/06/17/z6704423696987_15fd32ffc26d590d204d520c9dac6786-nongnghiep-093938.jpg)
(VAN) In Hue city, modern technology has recently been applied in meteorological and hydrological forecasting and warning, helping to reduce the damage caused by natural disasters.

(VAN) A cutting-edge farming technique being implemented on an experimental ranch in Arizona's Sonoran Desert has already saved a billion gallons of water over five years, according to Civil Eats.

(VAN) Poultry and pig production and the environment can be boosted through enhanced water technology, according to new research.