June 24, 2025 | 19:37 GMT +7
June 24, 2025 | 19:37 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
June 24, 2025 | 19:37 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
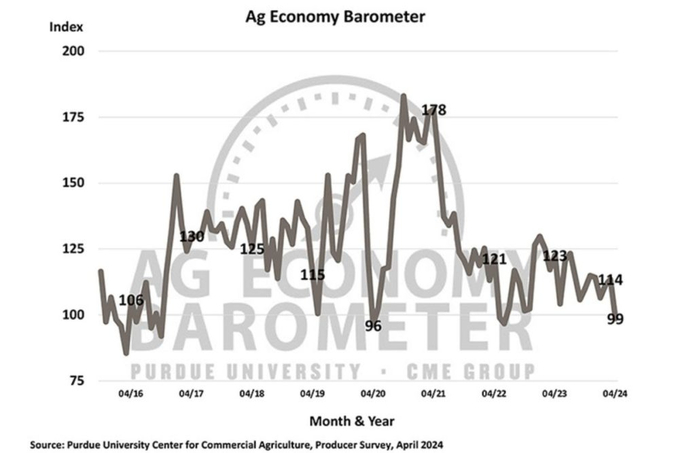
The sentiment decline was driven by worries regarding the current financial situation on farms and anticipated financial challenges in the coming year, said Jim Mintert.
The monthly survey of US farmers, conducted April 8-12, saw the barometer reading decline 15 points from March to 84, with both of its sub-indexes falling significantly.
The Current Condition Index dropped by 18 points to 83, while the Future Expectations Index fell by 14 points to 106. April marked the lowest farmer sentiment reading since June 2022 and the weakest current condition rating since May 2020.
The sentiment decline was driven by worries regarding the current financial situation on farms and anticipated financial challenges in the coming year, said Jim Mintert, the barometer’s principal investigator and director of Purdue University’s Center for Commercial Agriculture.
“Farmers’ sentiment took a significant hit in April, reflecting broader concerns about financial performance and farmland values,” Mintert said.
The Farm Financial Performance Index declined to 76 in April, marking a 7-point drop from the previous month and a 21-point decrease from last fall’s peak of 97. Mintert noted that this downturn reflects farmers’ growing concerns about the upcoming year’s financial outlook, with fewer respondents expecting better or equal performance than last year.
Farmers’ expectations regarding interest rates and farmland values shifted in April’s survey. Only 24% of respondents anticipate interest rates rising over the next year, down from 32% in March. Fewer farmers this month also said they expect to see farmland values rise over the next year, despite the modest improvement in their interest rate outlook, while more farmers reported that they look for farmland values to hold steady. In the April survey, just 29% of producers said they expect farmland values to rise in the upcoming year, compared to 38% who felt that way in March. These shifts reflect farmers’ concern about farm financial performance in 2024 outweighing their improved interest rate outlook.
There is growing interest in using farmland for solar energy production, and solar lease rates appear to be increasing. The survey revealed a 7-point uptick in respondents reporting discussions with companies about solar energy leases, reaching 19% compared with 12% in March. Specifically, discussions around solar leasing suggest demand for solar leases is increasing, with 58% of farmers reporting lease rate offers exceeding $1,000 per acre — up from 54% in March. Over one-fourth of respondents (28%) said they were offered a farmland lease rate of $1,250 or more per acre. Rising lease rates for energy production could be starting to impact farmland values, at least in some areas. Among producers who said they expect values to rise in the next year, 8% of respondents highlighted energy production as a key reason.
“Looking ahead, energy production activities could provide some support for farmland values and expectations in some regions,” Mintert said.
(WG)
(VAN) Researchers from the Institute of Applied Ecology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a new environmentally friendly fertilizer additive that significantly enhances crop yields while reducing emissions of harmful gases.

(VAN) Poultry production in Poland, which has only started recovering from devastating bird flu outbreaks earlier this year, has been hit by a series of outbreaks of Newcastle disease, with the veterinary situation deteriorating rapidly.

(VAN) Extensive licensing requirements raise concerns about intellectual property theft.

(VAN) As of Friday, a salmonella outbreak linked to a California egg producer had sickened at least 79 people. Of the infected people, 21 hospitalizations were reported, U.S. health officials said.

(VAN) With the war ongoing, many Ukrainian farmers and rural farming families face limited access to their land due to mines and lack the financial resources to purchase needed agricultural inputs.

(VAN) Vikas Rambal has quietly built a $5 billion business empire in manufacturing, property and solar, and catapulted onto the Rich List.

(VAN) Available cropland now at less than five percent, according to latest geospatial assessment from FAO and UNOSAT.