June 21, 2025 | 02:12 GMT +7
June 21, 2025 | 02:12 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
June 21, 2025 | 02:12 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918

Well before the COVID-19 pandemic, we were already not on track to meet our commitments to end world hunger and malnutrition in all its forms by 2030. Now, the pandemic has made this significantly more challenging.
After remaining virtually unchanged for five years, the prevalence of undernourishment (PoU) increased 1.5 percentage points in 2020 – reaching a level of around 9.9 percent, heightening the challenge of achieving the Zero Hunger target by 2030.
Compared with 2019, about 46 million more people in Africa, 57 million more in Asia, and about 14 million more in Latin America and the Caribbean were affected by hunger in 2020.
Around 660 million people may still face hunger in 2030, in part due to lasting effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on global food security – 30 million more people than in a scenario in which the pandemic had not occurred.
While the global prevalence of moderate or severe food insecurity has been slowly on the rise since 2014, the estimated increase in 2020 was equal to that of the previous five years combined. Nearly one in three people in the world (2.37 billion) did not have access to adequate food in 2020 – an increase of almost 320 million people in just one year.
Close to 12 percent of the global population was severely food insecure in 2020, representing 928 million people – 148 million more than in 2019.
The high cost of healthy diets coupled with persistent high levels of income inequality put healthy diets out of reach for around 3 billion people, especially the poor, in every region of the world in 2019.
Globally, malnutrition in all its forms also remains a challenge. Although it is not yet possible to fully account for the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, in 2020, it is estimated that 22.0 percent (149.2 million) of children under 5 years of age were affected by stunting, 6.7 percent (45.4 million) were suffering from wasting and 5.7 percent (38.9 million) were overweight. The actual figures are expected to be higher due to the effects of the pandemic. Africa and Asia account for more than nine out of ten of all children with stunting, more than nine out of ten children with wasting and more than seven out of ten children who are affected by overweight worldwide.
Globally, the world is not on track to achieve targets for any of the nutrition indicators by 2030. The current rate of progress on child stunting, exclusive breastfeeding and low birthweight is insufficient, and progress on child overweight, child wasting, anaemia in women of reproductive age and adult obesity is stalled or the situation is worsening.
Conflict, climate variability and extremes, and economic slowdowns and downturns (now exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic) are major drivers of food insecurity and malnutrition that continue to increase in both frequency and intensity, and are occurring more frequently in combination.
The reversal in the PoU trends in 2014 and continuous increase are largely attributed to countries affected by conflict, climate extremes and economic downturns, and to countries with high income inequality. Between 2017 and 2019, the PoU increased by 4 percent in countries affected by one or more of these major drivers while it decreased by 3 percent in countries not affected by them. High income inequality magnified this negative impact of the drivers, particularly in middle-income countries.
In the same period, countries affected by multiple drivers exhibited the highest increases in the PoU, 12 times larger than those in countries affected by only a single driver. Drivers that are external (e.g. conflicts or climate shocks) and internal (e.g. low productivity and inefficient food supply chains) to food systems are pushing up the cost of nutritious foods which, combined with low incomes, are increasing the unaffordability of healthy diets, particularly in countries affected by multiple drivers.
Because these major drivers are negatively affecting food security and nutrition by creating multiple, compounding impacts throughout our food systems, a food systems lens is essential to better understand their interactions and identify entry points for interventions to address them.
Depending on context, there are six pathways to follow towards food systems transformation: integrating humanitarian, development and peacebuilding policies in conflict-affected areas; scaling up climate resilience across food systems; strengthening resilience of the most vulnerable to economic adversity; intervening along the food supply chains to lower the cost of nutritious foods; tackling poverty and structural inequalities, ensuring interventions are pro-poor and inclusive; and strengthening food environments and changing consumer behaviour to promote dietary patterns with positive impacts on human health and the environment.
Given that most food systems are affected by more than one driver, the formulation of comprehensive portfolios of policies, investments and legislation may be elaborated along several pathways simultaneously. This will allow for maximizing their combined effects on food systems transformation, exploiting win-win solutions and mitigating undesirable trade-offs. Coherence in the formulation and implementation of policies and investments among food, health, social protection and environmental systems is also essential to build on synergies towards more efficient and effective food systems solutions.
Systems approaches are needed to build coherent portfolios of policies, investments and legislation and enable win-win solutions while managing trade-offs, including territorial approaches, ecosystems approaches, Indigenous Peoples’ food systems approaches and interventions that systemically address protracted crisis conditions.
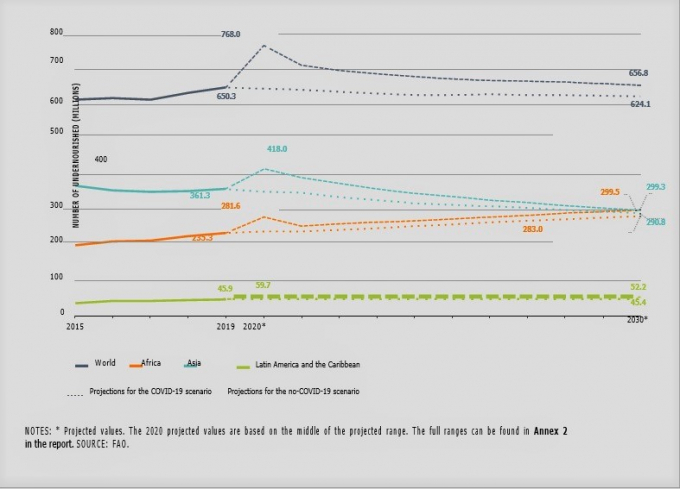
The Covid-19 scenario projects a small decrease in global hunger between 2021 and 2030, with wide variation in evolution across regions.
While 2020 was an immense challenge for the world, it may also be a warning of unwelcome events to come if more resolute actions to change course are not taken because the major drivers have their own trajectory or cyclicality and will continue to occur.
The UN Food Systems Summit 2021 will bring forward a series of concrete actions to support a transformation of the world's food systems. The six transformation pathways identified in this report are needed for greater resilience to specifically address the negative impacts of the major drivers behind the recent rise in hunger and slowing progress to reduce malnutrition in all its forms.

(VAN) Poultry production in Poland, which has only started recovering from devastating bird flu outbreaks earlier this year, has been hit by a series of outbreaks of Newcastle disease, with the veterinary situation deteriorating rapidly.

(VAN) Extensive licensing requirements raise concerns about intellectual property theft.

(VAN) As of Friday, a salmonella outbreak linked to a California egg producer had sickened at least 79 people. Of the infected people, 21 hospitalizations were reported, U.S. health officials said.

(VAN) With the war ongoing, many Ukrainian farmers and rural farming families face limited access to their land due to mines and lack the financial resources to purchase needed agricultural inputs.

(VAN) Vikas Rambal has quietly built a $5 billion business empire in manufacturing, property and solar, and catapulted onto the Rich List.

(VAN) Available cropland now at less than five percent, according to latest geospatial assessment from FAO and UNOSAT.

(VAN) Alt Carbon has raised $12 million in a seed round as it plans to scale its carbon dioxide removal work in the South Asian nation.