April 3, 2025 | 14:55 GMT +7
April 3, 2025 | 14:55 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
April 3, 2025 | 14:55 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
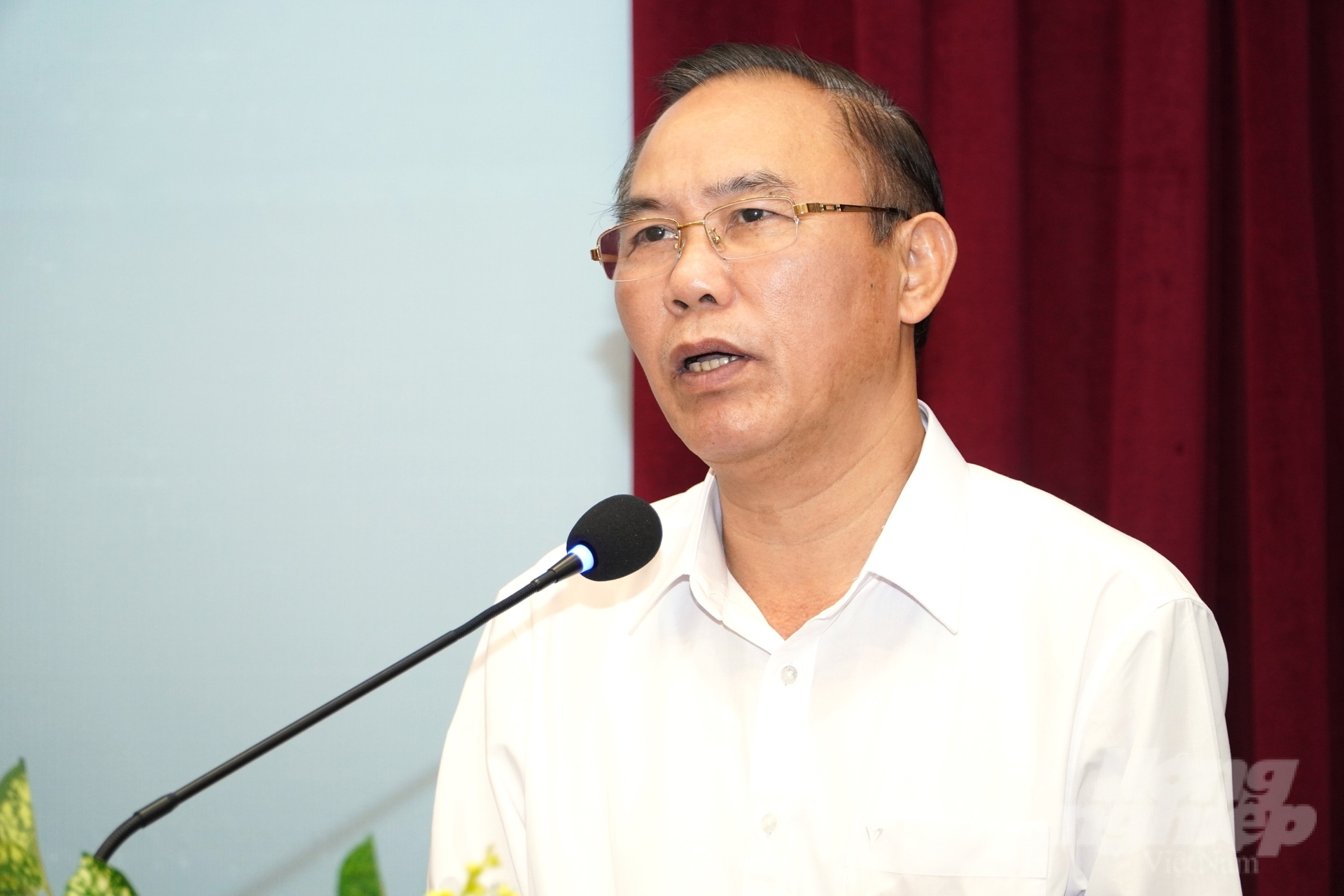

Deputy Minister of Agriculture and Rural Development, Mr. Phung Duc Tien, has instructed the animal health sector to rigorously carry out the review, inspection, and post-inspection of biological products. Photo: Kim Anh.
The nationwide aquaculture area affected by diseases in the first nine months of 2023 has increased by 12.3% compared to the same period in 2022, which is equivalent to over 22,500 hectares. The majority of the damage occurred in shrimp farming areas, accounting for up to 88%.
The main dangerous diseases affecting shrimp include White Spot Disease and Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease. However, these diseases have shown a decreasing trend compared to 2022. In certain farming areas within the provinces of Soc Trang, Kien Giang, and Ca Mau, there have been reports of viral infections with high risks of spreading to neighboring regions. In addition to direct disease outbreaks, environmental changes and weather fluctuations have contributed to the damage to aquaculture areas.
During a conference on developing aquaculture solutions held in Can Tho City, Deputy Minister of Agriculture and Rural Development Phung Duc Tien stressed that biological products are being sold extensively on the market as disease control agents.
In several cases, these products have facilitated the sale of low-quality goods, resulting in high mortality rates among shrimp and pangasius. Consequently, Deputy Minister Tien raised the issue regarding the effective performance of review, inspection, and post-inspection activities.
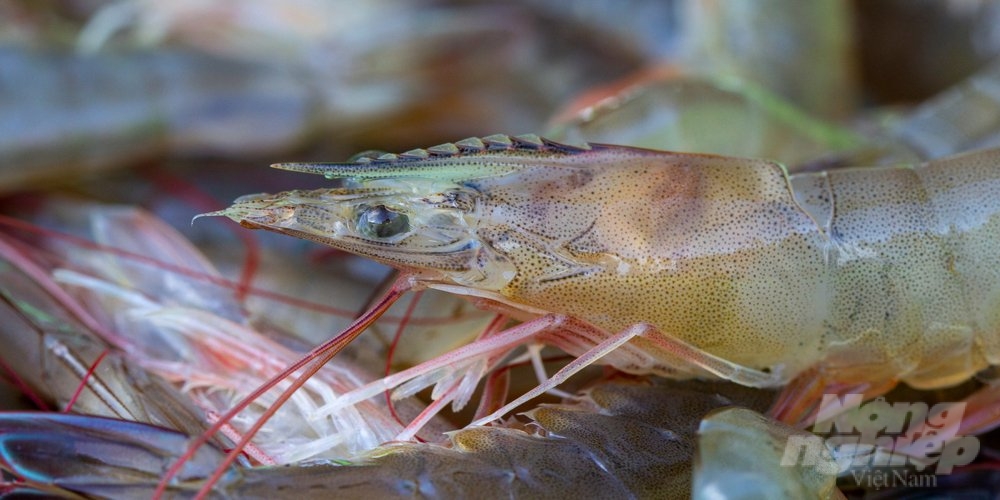

Dangerous diseases affecting shrimp have shown a decreasing trend compared to 2022. Photo: Kim Anh.
Mr. Phung Duc Tien have called for strict control over the trading of aquatic biological products in aquaculture and for a collective effort to address this issue. Subsequently, he aims to provide guidance, warnings, and training to fish farmers.
Vaccination is a crucial safeguarding measure in aquacultural production. There is currently no vaccine available for shrimp, crustaceans, or mollusks worldwide. There are pangasius vaccinations on the market in Vietnam. Additionally, there are plans to provide vaccines for several freshwater fish species.
Disease prevention measures in shrimp farming primarily involve using disease-free broodstock, enforcing biosecurity measures at facilities, pond management, and developing region-specific farming practices. Additionally, advanced techniques are utilized to prevent diseases from entering the farming areas.
Although many scientific research and technological solutions have been explored to combat shrimp diseases, no substantial results have been found. The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development plans to rigorously review and assess scientific research and technology projects in order to ensure that they offer optimal and effective solutions for farmers and businesses.
The Department of Animal Health under Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development has urged local governments to proactively allocate resources for disease monitoring. Accordingly, 42 provinces and cities across Vietnam have established plans for aquatic disease prevention in 2023. However, only 21 of them have allocated more than 40 billion VND for this endeavour.
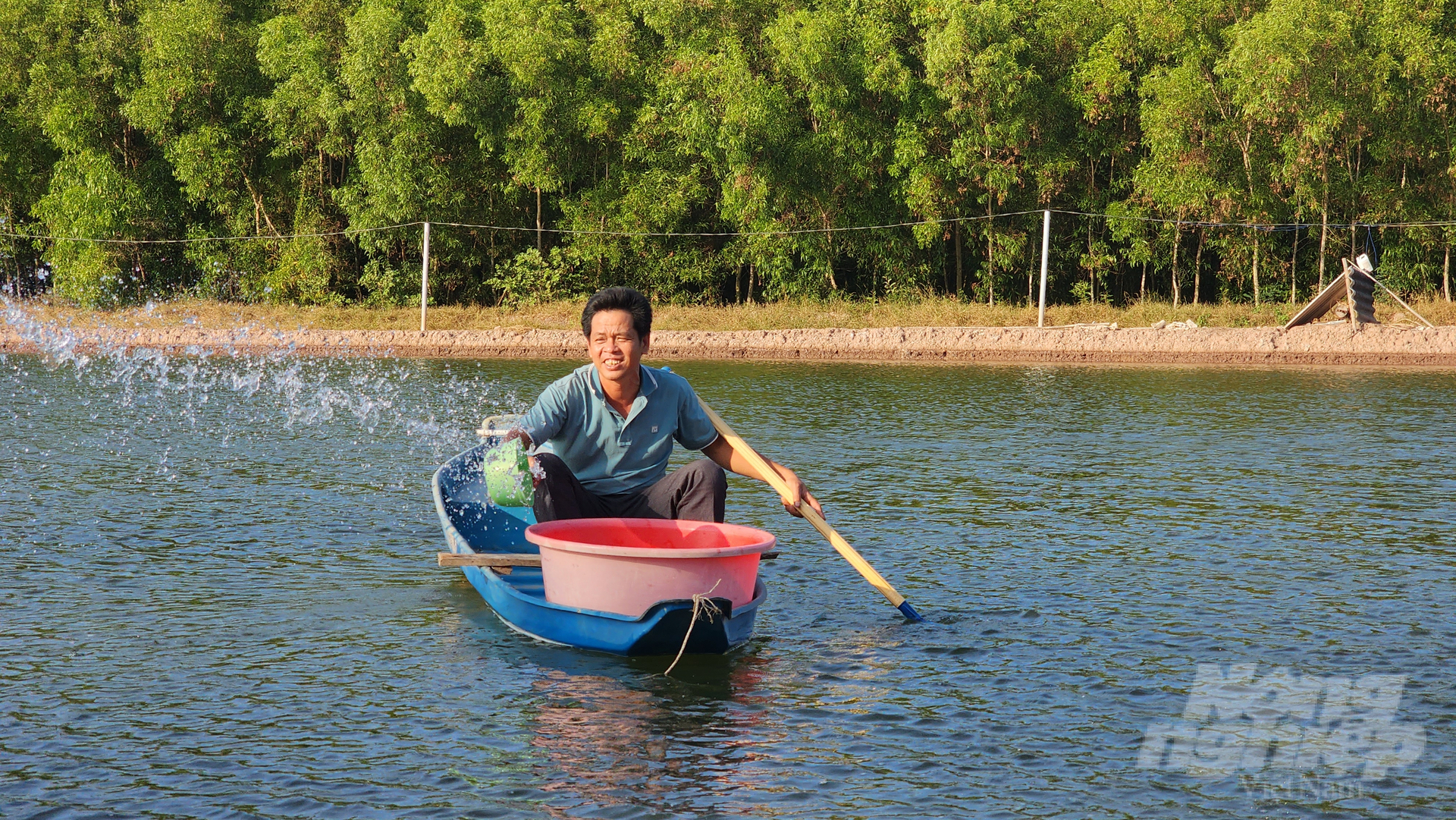

The Department of Animal Health has recommended that local authorities and businesses intensify proactive disease monitoring on shrimp, catfish, and other economically valuable species.
Mr. Nguyen Ngoc Tien, Head of Aquatic Animal Health at the Department of Animal Health, assessed that these resources are insufficient for the implementation of disease prevention and control measures, especially the proactive monitoring and collection of samples for testing to determine the causes of mass aquatic animal deaths.
Most notably, certain provinces and cities only allocate funds when diseases occur instead of focusing on the prevention aspect. After a reviewing process, Deputy Minister Phung Duc Tien has disclosed that the budget for preventing aquatic animal diseases accounts for approximately 8.34% of the total budget allocated for animal disease prevention efforts.
The Department of Animal Health recommends local governments and businesses to intensify proactive disease monitoring on shrimp, pangasius, and other economically valuable or widely cultured species towards the end of the year.
There are currently 32 disease-free facilities nationwide, including 32 shrimp production facilities (27 shrimp breeding facilities with an annual production capacity of 40 billion postlarvae and 3 commercial shrimp farming facilities) and 2 ornamental fish production facilities for export.
The Department of Animal Health will continue to support shrimp farming facilities in constructing disease-free facilities in accordance with regulations to facilitate exports.
In an effort to enhance the application of digital technology, Can Tho city has strengthened its efforts in updating information on aquatic animal disease within the Vietnam Animal Health Information System (VAHIS).
Translated by Nguyen Hai Long
![Sustainable future for wood industry: [Part 3] Green transformation](https://t.ex-cdn.com/nongnghiep.vn/608w/files/doanhtq/2025/04/01/2558-2129-4jpg-nongnghiep-162120.jpg)
(VAN) One of the solutions for Vietnam's timber industry to achieve sustainable development amid the current challenges is to undergo a green transformation…

(VAN) Empowering farmers, Indigenous Peoples, local communities and scientists to conserve and use genetic resources is key to resilient agrifood systems.

(VAN) Mr. Nguyen Do Anh Tuan, Director of the International Cooperation Department (Ministry of Agriculture and Environment), affirmed that ecological agriculture is a solution for many challenges in the current period.
(VAN) The project ‘Drought impact assessment in the Central Highlands’ will leverage remote sensing technology to forecast drought for about 1,500 square kilometers of agricultural production areas.

(VAN) The World Bank (WB) will accompany the Ministry of Agriculture and Environment in implementing sustainable fisheries infrastructure development and ensuring livelihoods projects.
![Sustainable future for wood industry: [Part 2] Businesses concern about tax policies](https://t.ex-cdn.com/nongnghiep.vn/608w/files/huytd/2025/03/28/2517-4-160407_111-092943.jpg)
(VAN) In addition to the challenges posed by the EUDR, Vietnam's wood industry is also facing tax policies from the United States, one of its major markets.
![Sustainable future for wood industry: [Part 1] Identifying challenges](https://t.ex-cdn.com/nongnghiep.vn/608w/files/tungvd/2025/03/16/5915-4jpg-nongnghiep-155905.jpg)
(VAN) With the European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) and fluctuations in the global market, Vietnam's wood industry will face numerous challenges in the coming years that must be overcome...