May 5, 2024 | 05:30 GMT +7
May 5, 2024 | 05:30 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
May 5, 2024 | 05:30 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
The spots are far more abundant in reared than in wild salmon, and their causes are poorly understood.
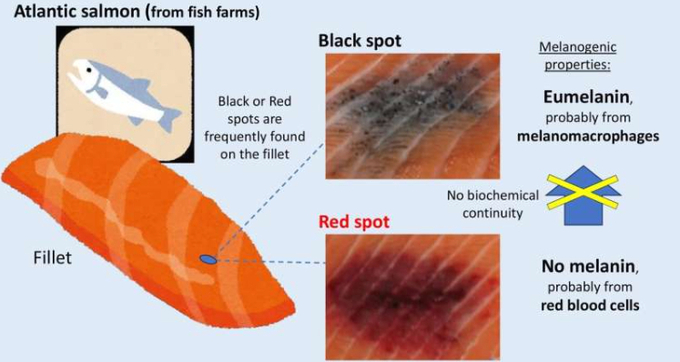
A substantial percentage of filets from reared Atlantic salmon have black or red spots. Wakamatsu and coworkers found that the black spots contain eumelanin, whereas the red spots do not detectably contain melanin.
Realizing that the biochemistry of the spots should be clarified, Professor Turid Mørkøre of the Norwegian University of Life Sciences turned to two leaders in melanin biochemistry science, Professor Kazumasa Wakamatsu and Professor Shosuke Ito of Fujita Health University, Japan.
These researchers found that the black spots contain melanin called eumelanin and that the red spots do not detectably contain melanin. The biochemical discontinuity between the red and black spots supports that their pigments derive from distinct cellular origins, being red blood cells and melanomacrophages (fish macrophages with dark pigment), respectively.
Although within expectations, the finding is an important step toward understanding the spots problem, and the study was published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
In the last decades, focal discolorations on filets from Atlantic salmon muscle have become an increasing problem for commercial seafood farming, affecting a substantial part of the filets. The reasons for the spots are mysterious, although several plausible theories have been put forward, and most likely there are multiple different causes. The spots are roughly categorized as either "red spots" or "black spots" and are also known as "red focal changes" and "melanized focal changes."
However, a proper biochemical analysis of the black spots had never been performed, and the suggestion of them containing melanin was mostly based on the staining with Fontana Masson which is only relatively specific for melanin. Intermediate forms between red spots and black spots have been found, leading to a concept shared by many that black spots are usually derived from red spots.
Melanin is a very large, highly irregular heteropolymer consisting of monomeric units derived from the enzymatic oxidation of the amino acid tyrosine, and there are several types of melanin. Professors Wakamatsu and Ito are melanin specialists who established a panel of biochemical assays for characterizing multiple types of melanin for different species, varying between human melanoma patients and fossilized animals like dinosaurs.
Applying these assays to spots on filets of Atlantic salmon from Norway, they found that the black spots contained the black pigment "eumelanin," which is also present in human hair and skin, whereas, for the red spots, they could not conclude the presence of melanin. In the red spots, however, they did find some DOPA-derived products that are suggestive of an oxidative environment consistent with hemorrhage.
Importantly, the findings by Wakamatsu et al. revealed that there is no biochemical continuity between the pigments of the red and black spots, which supports earlier histology-driven hypotheses that red spots are caused by hemorrhage and black spots by local accumulations of melanomacrophages in chronic local immune reactions.
Melanomacrophages are immune cells only found in ectothermic vertebrates, including fish, amphibians, and reptiles. By inference, the new study by Wakamatsu et al. implies that the black pigment in melanomacrophages is eumelanin, which had not been properly determined before.
Hemorrhages can have a variety of causes, not each hemorrhage leads to chronic inflammation with melanomacrophages, and melanomacrophages can also accumulate for reasons other than hemorrhage. Therefore, the distinct cellular origin of red and black spots, as supported by their biochemical discontinuity shown by Wakamatsu et al., implies that researchers should expect an assortment of possible causes for the different spots and not try to find a "one model-fits-all" explanation.
Professor Erling Koppang, a Norwegian specialist on salmon filet spots who was not involved in this study, explains, "The study by Wakamatsu and coworkers is an important component in the characterization of pigmented lesions in the Atlantic salmon and falls nicely in line with our group's previous identification of the expression of tyrosinase [a gene necessary for melanin production] in black changes."
"Now we know with certainty that the final product is as we have expected, which is important for moving forward in trying to prohibit these lesions."
(Phys)

(VAN) After more than a decade of discussion, the Food and Drug Administration has published a final rule for certain agricultural water used in the production of produce.

(VAN) Representatives with multiple agencies including the CDC, the United States Department of Agriculture and the Food and Drug Administration on May 1 discussed the latest news about bird flu in the U.S.

(VAN) Approved by the UN General Assembly, it will increase awareness of the crucial role women farmers play in agrifood systems.

(VAN) Chinese scientists have cut the growth cycle of a conventional rice variety in half in a desert greenhouse in Xinjiang, a welcome agricultural innovation for Beijing as it seeks new methods to ensure food security.
(VAN) Preliminary results of tests on additional dairy products show that pasteurization inactivates the bird flu virus, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration said on Wednesday.
(VAN) At UNGA-ECOSOC event, FAO Deputy Director-General emphasizes the key role of anticipatory action in protecting and equipping communities ahead of shocks.

(VAN) Despite protein reduced poultry feed – better performance parameters and less burden for the environment!