June 22, 2025 | 05:25 GMT +7
June 22, 2025 | 05:25 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
June 22, 2025 | 05:25 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918

Ms. Pham Thi Mai Huong from the Bioversity & CIAT Alliance spoke at the training workshop on enhancing food safety communication, co-hosted by Vietnam Agriculture Newspaper and International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI). Photo: ILRI.
According to Dr. Pham Thi Mai Huong from the Bioversity & CIAT Alliance, “A sustainable food system ensures food and nutrition security for the entire society by providing food that meets both quality and quantity standards. At the same time, this system creates a favorable environment for all stakeholders, from producers and distributors to retailers, thereby strengthening a solid socio-economic foundation.”
Furthermore, a healthy diet not only helps prevent malnutrition but also reduces the risk of non-communicable diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. According to FAO (2022), approximately 30% of Vietnam's population cannot afford a healthy diet. Therefore, improving dietary patterns is a critical strategy for ensuring sustainable health for all.
A sustainable food system not only ensures food supply but also delivers socio-economic benefits, improves livelihoods for stakeholders from farmers to retailers. Photo: CIAT.
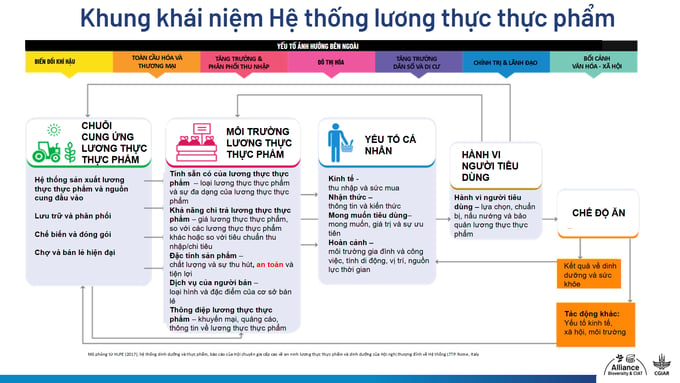
The conceptual framework for the global food system includes key components such as production, harvesting, processing, packaging, consumption, and waste management. A sustainable food system not only ensures food supply but also delivers socio-economic benefits, improves livelihoods for stakeholders from farmers to retailers, and minimizes negative environmental impacts.
Ms. Pham Thi Mai Huong further stated, "Vietnam has performed well in terms of food production, while food safety aspects are being gradually improved according to a set pathway. This progress is expected to drive improvements in diversity and quality within the food system."
A healthy diet is built on four key factors: (i) production: ensuring adequate energy supply; (ii) diversity: covering all food groups such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals; (iii) quality: providing essential nutrients and sufficient calories; (iv) food safety: ensuring hygiene and the absence of harmful substances.
An ideal food system must meet consumer demands for food safety and quality while promoting socio-economic well-being and reducing ecological pressure. Achieving this requires collaboration among stakeholders, including producers, retailers, regulators, and communities.
Achieving the ideal outcome involves trade-offs. However, through cross-sector collaboration and effective interventions, we can move closer to building a sustainable and healthy food system, contributing to public health and environmental protection.
First, food supply chain plays a vital role in transferring food from production to consumption. Each stage, from production to distribution, impacts food safety and quality.
Second, the food environment acts as an intermediary, determining consumer access to and affordability of food. Key factors like food availability, price, and diversity are crucial to the safety and nutritional value of the food system.
Third, consumer behavior is strongly influenced by health awareness, personal preferences, and convenience. Food choices often depend on availability within the food environment. Thus, raising awareness and fostering a healthy food environment are essential to improving dietary habits.
Translated by Kieu Chi
![Turning wind and rain into action: [11] Ten years before storms, after every harvest](https://t.ex-cdn.com/nongnghiepmoitruong.vn/608w/files/news/2025/06/20/z6704423696987_15fd32ffc26d590d204d520c9dac6786-nongnghiep-140922.jpg)
(VAN) With WeatherPlus, every raindrop and every breeze carries a message. And if we learn to listen, the fields will no longer live in fear of the weather.
![Turning wind and rain into action: [10] Advancing accessible climate services for farmers](https://t.ex-cdn.com/nongnghiepmoitruong.vn/608w/files/linhnhp/2025/06/20/1911-z6704423696987_15fd32ffc26d590d204d520c9dac6786-nongnghiep-161854.jpg)
(VAN) Not only does it help farmers 'avoid droughts and rains,' the development of agricultural climate services also enhances their ability to proactively adapt to a rapidly changing climate.

(VAN) With international assistance, the harvesting of sargassum seaweed in Quang Ngai has become increasingly regulated, thereby safeguarding marine life and ensuring the stability of coastal communities' livelihoods.

(VAN) On June 19, the United Kingdom officially became a Development Partner of the Mekong River Commission.

(VAN) Biodiversity is being threatened by traditional remedies made from wildlife. Traditional medicine and humans must change to live in harmony with nature.

(VAN) Agrifood investment and finance solutions for people and the planet.

(VAN) Microplastic contamination has become pervasive in seafood, posing unprecedented challenges for food safety and marine ecosystems.