June 17, 2025 | 10:40 GMT +7
June 17, 2025 | 10:40 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
June 17, 2025 | 10:40 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
Mekong Delta's strategic development is threatened by salinity, depression, erosion, water quality, and biodiversity loss.
WWF Vietnam specialists disclosed recent research excavations demonstrating that a lack of sedimentary rock is the primary cause of river bed and bank erosions, coastal erosion, and salinity. The situations are the result of hydroelectric development and sand extraction in the upper Mekong basin.

Research excavations demonstrating that a lack of sedimentary rock is the primary cause of river bed and bank erosions, coastal erosion, and salinity. Photo: Kim Anh.
Typically, by the end of 2022, the entire Mekong Delta will have 596 riverbank landslides measuring nearly 583 kilometers in length and 48 coastal landslides measuring 221.7 kilometers in length. Up to 99 of these points are classified as especially hazardous. This situation has a direct impact on the socioeconomic status of millions of Mekong Delta residents.
The construction of a sand bank for the Mekong Delta has been concluded after nearly twenty months of research, surveying, measuring, data analysis, and consultation with pertinent parties. This is the world's first research endeavor to encompass the entire delta.
Specifically, WWF Vietnam's research team conducted measurements along 550 kilometers of the Tien and Hau rivers and collected sediment samples from the riverbed along with other exploration data.
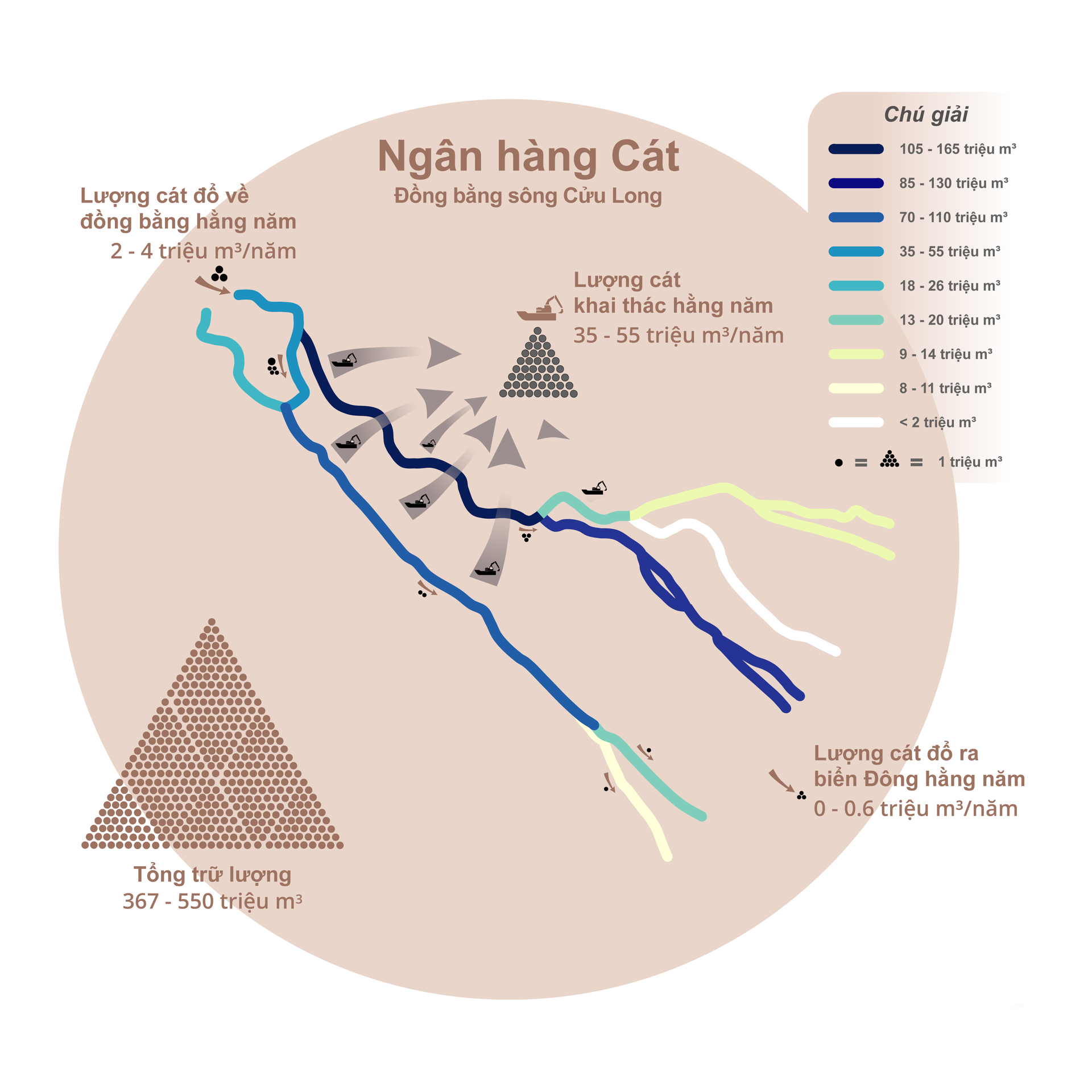
Sand bank for the Mekong Delta. Photo: WWF Vietnam.
Recorded results indicate that the total sand reserves of the Mekong Delta are estimated at about 367 - 550 million m3 (primarily based on the unfixed sand layer). This is the quantity of sediment that has accumulated over hundreds of years and is crucial to the stability of the delta.
The 2022 survey reveals that between 0 and 0.6 million m3 of sand is deposited annually in coastal areas. Meanwhile, the quantity of sand flowing into the delta from upstream has decreased to 2 to 4 million m3/year due to hydroelectric structures capturing most of it upstream. This is significantly less than the present sand exploitation rate of 35 to 55 million m3/year (equivalent to nearly 50 percent of the total sediment flowing into the Mekong Delta).
Research indicates that, if the present rate of exploitation is maintained, the supply of sand from upstream to the delta will be limited. In the next ten years, the Mekong Delta's sand reserves will be depleted, which will have a severe impact on the delta's morphological stability and resilience.
Moreover, based on existing salinity forecasts, the joint venture expert group Deltares, a consulting unit on building a sandbank for the Mekong Delta, warns that the loss of 500 million cubic meters of sediment from the river system of the Mekong Delta could increase the number of areas affected by saline intrusion in the region by 10 to 15 percent.

On September 29, WWF Vietnam coordinated with partners to announce the results of building a sand bank in Can Tho City. Photo: Kim Anh.
According to Mr. Ha Huy Anh, National Manager of the Sustainable Sand Management Project in the Mekong Delta for WWF Vietnam, this is the first time that Vietnam has sand balance data for the entire Mekong Delta. Although the above measurements were conducted for only one year, they provide a limited overview of the Mekong Delta's current sediment situation. From there, support the authorities in planning policies for sustainable sand mining management in the Mekong Delta, and develop a plan to reduce the Mekong Delta's vulnerability to climate change and human impacts.
Mr. Marc Goichot, Freshwater Program Manager, WWF Asia-Pacific, recommends, based on the results of building cross-border and inter-provincial sandbanks for the Mekong Delta, the establishment of a centralized management plan on a regional scale, as opposed to the current system of management and licensing by each province. In addition, it encourages the research and development of sustainable substitute materials.

Mr. Ha Huy Anh, National Manager of the Sustainable Sand Management Project in the Mekong Delta for WWF Vietnam, this is the first time that Vietnam has sand balance data for the entire Mekong Delta. Photo: Kim Anh.
WWF Vietnam will share data, results, and recommendations with relevant collaborators in the near future. At the same time, search for opportunities to expand sandbanks from the delta scale to the basin level, for comprehensive sand management. Moreover, it is necessary to develop environmentally favorable and cost-effective alternatives to river sand with larger reserves and volumes than the current period.
Building a Sand Bank for the Mekong Delta is part of the Project "Mitigating climate change impacts and preventing natural disasters through public-private sector participation in sustainable sand mining in the Mekong Delta." WWF Vietnam, in collaboration with the Department of Dyke Management and Natural Disaster Prevention (MARD), has been implementing the project since 2019, with completion anticipated by mid-2024.
The initiative is funded by the International Climate Initiative Fund of the German Government through WWF Germany, contributing to the preservation of vital ecological functions and the minimization of socioeconomic hazards resulting from climate change in the Mekong Delta.
Sandbank research results will continue to be used to develop a plan to maintain stable river morphology in the Mekong Delta, which will include recommendations and guidance on sustainable and integrated sand and gravel exploitation, as well as the integration of policies on natural disaster prevention and sustainable development in the Mekong Delta.
Translated by Linh Linh

(VAN) According to the Binh Thuan Department of Industry and Trade, in the first five months of 2025, Binh Thuan's dragon fruit export turnover increased by 20.65% compared to the same period last year.

(VAN) EU countries on Thursday gave final approval to new tariffs on fertilizer imports from Russia, a move aimed at cutting off revenue that could support Moscow’s war in Ukraine, despite concerns from European farmers.

(VAN) The working delegation from the Ministry of Agriculture and Environment conducted an important trip to the Netherlands to strengthen strategic partnerships and sustainable development in the agricultural sector.

(VAN) The letter ‘A Plea from the Ocean’ not only evokes emotion but also awakens the human conscience to the responsibility of protecting life on Earth.
(VAN) The Department of Agriculture in South Africa has announced the country’s first mass vaccination of poultry to prevent local birds from contracting avian influenza.

(VAN) Establishment of the Mekong Delta Regional Agricultural Linkage Center, aiming for a closed value chain, deep processing, trading platforms, and international market connectivity.

(VAN) Gia Lai province has recently recorded 460 rare species of animals and plants, contributing to forest conservation and biodiversity planning in the region.