May 19, 2025 | 01:30 GMT +7
May 19, 2025 | 01:30 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
May 19, 2025 | 01:30 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza viruses have been found in the yolk and albumen of eggs from infected chickens, turkeys and quails. Complementary to biosecurity, vaccination has become the primary control measure used to minimise losses . The objective of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of Mefluvac H5 Plus 8 against circulating HPAI H5N6 and H5N8 viruses isolated in Vietnam, adopting 2 vaccination regimes.
Avian influenza viruses type A are members of the family Orthomyxoviridae, being structured with a negative-sense, single-strand, segmented genomic RNA. The outer viral coat is characterised by the presence of two important antigenic fractions, the hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) proteins. Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) viruses can be originated from certain LPAI viruses while these are circulating in poultry flocks. HPAI viruses can cause mortality in 100% of the flock, and trigger epidemics that may spread rapidly, devastate the poultry industry and result in severe trade restrictions.
Animals: 3-week-old commercial chickens were purchased from a local farm in Vietnam with no avian influenza (AI) vaccination history. Before the experiments, birds were randomly checked for H5 antibodies and avian influenza virus (AIV) by RT-PCR test (10% of birds), obtaining negative results.
Vaccine: Mefluvac H5 Plus 8
Challenge viruses:
Used HI antigens: 3 weeks after each vaccine shot (at age of 6 and 9 weeks-old), all vaccinated birds were tested for antibody titers (H5 vaccine-homologous antigens).
Monitoring: Challenged chickens were monitored for 10 days after inoculation and scored for clinical signs in accordance with the WOAH guidelines.
Clinical protection and viral load reduction
The described figures (2A – 2B and 3A – 3B) concisely show i) the survival rate of vaccinated birds against virulent influenza viruses, and ii) the ability of reducing viral excretion; both considered important criteria when evaluating the efficacy of AI vaccines. The viral load was investigated by the analysis of oro-pharyngeal swabs after challenge.
Figure 2A and 2B – Challenge by HPAI H5N8 clade 2.3.4.4b at day 21 post-vaccination.
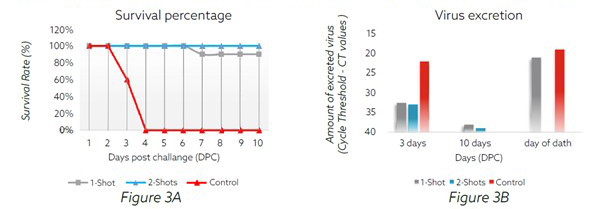
In the present study, we found that a vaccination regime with Mefluvac H5 Plus 8 inactivated vaccine triggered a strong immune response in experimental birds with homologous HI antibody titer of 6.6 log2 when used with 1-shot regime and 8.9 log2 when used with 2-times vaccination regime. After challenge with H5N8 clade 2.3.4.4b virus, Mefluvac H5 Plus 8 vaccine conferred a protective rate of 90% with both vaccination regimes: 1-shot and 2-shots. After challenge with H5N6 clade 2.3.4.4g virus, Mefluvac H5 Plus 8 vaccine conferred a protective rate of 90% for 1-shot vaccinated chickens and 100% protection for those birds receiving the 2-times vaccination regime.
(Poultryworld)

(VAN) 14 out of 35 domesticated elephants in Dak Lak province have had their living conditions improved, with 11 of them currently participating in the non-riding elephant tourism model.

(VAN) Muong Nhe Nature Reserve hopes that being upgraded to a national park will lay the foundation for forest protection efforts to be carried out in a systematic, modern, and sustainable manner.
/2025/05/16/3923-2-171845_52.jpg)
(VAN) Lower costs, higher yields, and improved soil quality are outstanding benefits that soybeans bring when integrated into the crop rotation system.

(VAN) The 'For a Green National Environment' programme aims to promote a green lifestyle, support businesses in implementing ESG practices, and turn Net Zero commitments into concrete actions.

(VAN) Cold-barn systems efficiently manage environmental and temperature conditions, which aids in the prevention of respiratory diseases in pigs and protects them from the vectors that transmit African swine fevers.

(VAN) To tackle challenges, the project 'Addressing key technical bottlenecks in the grouper supply chain in Vietnam' has been underway since 2024.

(VAN) The project 'Disease-Resilient and Sustainable Cassava Production Systems in the Mekong Region', funded by the Australian Center for International Agricultural Research (ACIAR), is being implemented from 2024 to 2028.