May 31, 2025 | 21:32 GMT +7
May 31, 2025 | 21:32 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
May 31, 2025 | 21:32 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
A national meeting on agroecological transition, organized by the Agroecology Learning Alliance in Southeast Asia (ALiSEA) in Vietnam, took place on November 13. This meeting served as a platform for member organizations to exchange experiences and knowledge, enhancing professional capacity to advance agroecological transformation.
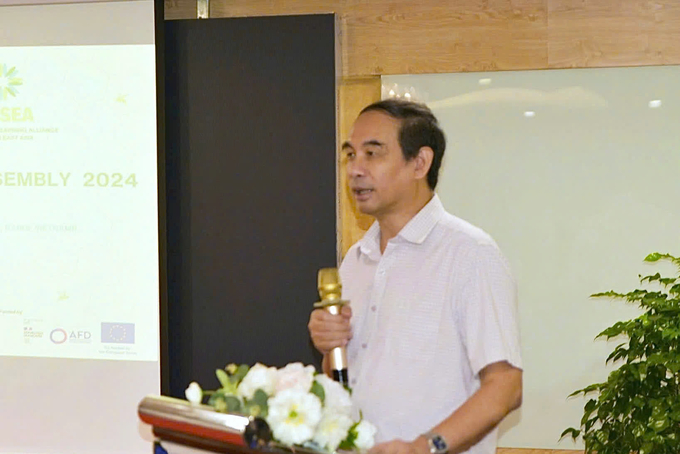

Associate Professor Dr. Dao The Anh, Deputy Director of the Vietnam Academy of Agricultural Sciences, spoke about the development of ecological agriculture and sustainable food systems. Photo: Kieu Chi.
In the meeting, Associate Professor Dr. Dao The Anh, Deputy Director of the Vietnam Academy of Agricultural Sciences and Vice President of the Vietnam Rural Development Science Association, emphasized the importance of transitioning to agroecology. The establishment of an ecological agriculture network in Vietnam is essential for developing agroecological models, including circular agriculture, climate change-resilient farming, and agroforestry.
Building a sustainable agroecological system requires unified voices, research, and scientific innovation. Currently, many research institutions and enterprises within the ALiSEA network are investing intellectual resources to find solutions and apply science to promote the development of agroecology. ALiSEA’s contributions play a vital role in shaping policies, guiding, and scaling up sustainable agriculture in local areas.
"The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development also shows readiness to listen to and support major initiatives aimed at promoting sustainable agriculture nationwide in fields such as livestock, aquaculture, and forestry," Associate Professor Dr. Dao The Anh said.
In terms of policy, the Institute of Policy and Strategy for Agriculture and Rural Development has supported localities such as Dong Thap and Son La province in developing agroecological transition plans at the provincial level and building sustainable food systems. Agroecological transformation models from the Agroecology and Safe food System Transitions (ASSET) project have been implemented, helping local areas adopt environmentally friendly farming methods and improve economic efficiency.
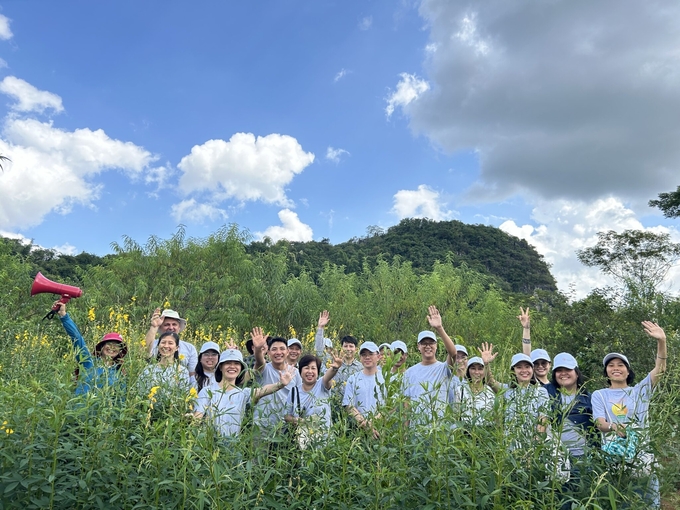

ALiSEA calls for strong participation to expand agroecological models. Photo: ALiSEA.
Ms. Lucie Reynaud, ALiSEA's regional coordinator, noted that over the past two years, ALiSEA has achieved positive results, and the network is working together to build a strategy for the coming years, including a 2025 action plan to promote sustainable development in ecological agriculture.
The 2025 development and action plan will focus on four main strategic components: capacity building through training programs and expansion mechanisms; encouraging active participation from stakeholders across the supply chain in agroecological development; raising consumer awareness and support for agroecological agriculture through mass media and a strategy to engage the press; assessing training needs and building a network for youth engagement, with activities that survey the needs of farmers and young people while creating exchange opportunities between organizations within the agroecological network in Vietnam and the region; and finally, establishing policy dialogues to facilitate knowledge transfer and training support in agroecological agriculture.
ALiSEA calls for robust participation from all parties, enabling widespread implementation of agroecological agriculture models. The network’s efforts not only contribute to environmental improvement but also provide economic benefits to farmers, encourage the development of safe and eco-friendly production methods, and promote sustainable agriculture in the region.
Translated by Kieu Chi

(VAN) For the durian industry to succeed, the value chain must fulfill its commitments to the government, the community, and international partners.
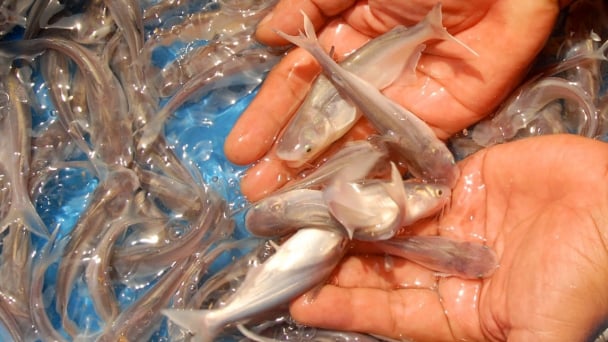
(VAN) Vaccinating juvenile pangasius helps reduce disease, antibiotic use, and farming costs, increasing profits for export-oriented farmers in An Giang.

(VAN) Due to a limited supply of workforce and competitive recruitment requirements, businesses struggle to retain talented veterinary human resources.

(VAN) WOAH’s guidance aims to mitigate disease risks through a One Health approach that balances economic, conservation, and public health interests.

(VAN) Ms. Nguyen Thi Dung, Deputy Director of Ngoc Hoang Cooperative, shared about the journey of bringing dragon fruit to Europe, achieving annual revenues in the billions of VND.

(VAN) Bamboo products from Thang Tho Bamboo Cooperative have reached many countries around the world, while also creating jobs for local workers.

(VAN) The Management Board of Con Dao National Park reported that a green sea turtle, tagged in the Philippines, has traveled thousands of kilometers to lay 84 eggs on Bay Canh Islet.