May 29, 2025 | 09:13 GMT +7
May 29, 2025 | 09:13 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
May 29, 2025 | 09:13 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
Currently, regulations on importing animal meat and meat products are basically perfect, including: the Law on Veterinary Medicine and documents guiding the implementation of the Law on Veterinary Medicine; the Food Safety Law and documents guiding its implementation; other relevant laws; and regulations of the World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH or OIE), the World Trade Organization (WTO) with Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) Agreement, and exporting countries.
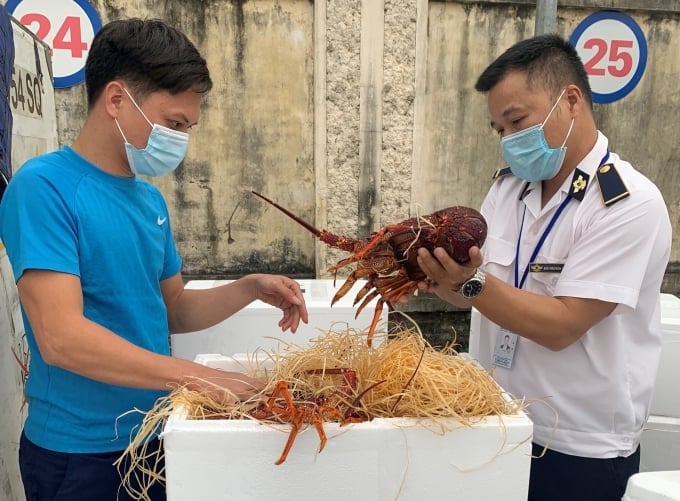

Animal quarantine officers (Department of Animal Health) inspect Australian lobsters imported at Noi Bai International Airport.
To be more specific, first, to be able to export animal meat and meat products to Vietnam, the exporting country needs to provide the Department of Animal Health with national records such as documents, data, and information about the disease situation; programs and results on disease surveillance; programs and results on food safety inspection for meat products; diagnostic and testing capacity; etc., to serve the evaluation of import risks.
If the results of evaluating import risks show that the exporting country meets Vietnam's disease safety and food safety requirements in accordance with international regulations, the Department of Animal Health will organize an inspection delegation to check reality in the exporting country, agree on import conditions, and agree with the competent veterinary agency of the exporting country on the form of a quarantine certificate for exporting meat to Vietnam.
Second, slaughter and meat processing factories of countries with a demand for exporting to Vietnam must be inspected by the competent veterinary agency of the exporting country for disease conditions, veterinary hygiene, and food safety. Then, the records of each factory must be sent to the Vietnam Department of Animal Health for appraisal.
Third, the Department of Animal Health conducts appraisal, inspection, and evaluation of each factory's export registration record (combined with actual inspection when necessary). If the factories meet the requirements, they will be included in the list of factories allowed to export meat to Vietnam. The appraisal and evaluation are carried out according to the provisions of the Government’s Decree 15/2018/ND-CP dated February 2, 2018, guiding the implementation of food hygiene and safety inspections of imported animal-derived goods and other relevant laws.
Thus, frozen animal meat and meat products, before being allowed to import into Vietnam, must go through the above-mentioned evaluation steps, with an evaluation period of at least 5 years.
Fourth, the quarantine of imported meat and meat products is carried out according to the regulations in Circular 09/2022/TT-BNNPTNT dated August 19, 2022; Circular 35/2018/TT-BNNPTNT dated December 25, 2018; and Circular 25/2016/TT-BNNPTNT dated June 30, 2016 of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development.
Accordingly, all frozen meat shipments imported into Vietnam are stored at the import border gate area and strictly inspected and controlled by the border veterinary agency.
The border veterinary agency takes samples of each batch of imported meat to test for pathogens according to regulations. If the test results meet the requirements, the batch will be allowed to be imported into Vietnam for domestic consumption.
The control of diseases and food hygiene and safety for animal meat products and other types in general from exporting countries to Vietnam are very closely organized.
Fifth, every year, the Department of Animal Health presides over the development of plans and monitoring content and submits them to the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development for approval and funding for implementation. Report to the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development on monitoring and sample analysis results and an implementation plan for the next year.
In addition, issue a written notice to competent authorities in the country importing animal products when required; issue a written notice to the competent veterinary agency of the exporting country requesting to investigate the cause, take corrective actions, and send a report to the Department of Animal Health when the monitoring sample does not ensure food safety according to Vietnamese regulations.
It can be seen that the control of diseases and food hygiene and safety for animal meat products and other types in general from exporting countries to Vietnam are very strictly organized in accordance with regulations.
Vietnam imports meat and meat products from 37 markets around the world. In particular, India is the largest market supplying meat and meat products to Vietnam, accounting for 29.53% of the country's total imported meat and meat products.
In January 2024, Vietnam mainly imported categories such as: Meat and edible offal of fresh chilled or frozen poultry; fresh frozen buffalo meat; Edible post-slaughter by-products of chilled or frozen live pigs, buffaloes and cows; fresh chilled or frozen pork; Fresh chilled or frozen beef…
Translated by Huyen Vu Thu

(VAN) The mutual export of agrifood products between the European Union (EU) and the United Kingdom (UK) must occur again without certification, border controls or other red tape. This was agreed at the UK-EU summit.
/2025/05/22/5121-2-173645_677.jpg)
(VAN) NBSAP Tracker identifies strengths and areas for improvement in the National Biodiversity Strategy, based on each region’s priorities and capacities.

(VAN) The draft amendment to the Circular on rice export trading stipulates a periodic reporting regime for rice exporting enterprises.

(VAN) Dong Thap farmers attained an average profit margin of 64% during the summer-autumn 2024 crop (first season), while An Giang and Kien Giang farmers followed with 56% and 54%, respectively.

(VAN) As a doctoral student doing research on renewable energy and electrification at Harvard University, the author shares his musings on electricity, nature, and countryside memories.

(VAN) The decree on Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) ensures transparent management and disbursement of support funds, avoiding the creation of a “give-and-take” mechanism.

(VAN) Hue City rigorously enforces regulations regarding marine fishing and resource exploitation, with a particular emphasis on the monitoring of fishing vessels to prevent illegal, unreported, and unregulated (IUU) fishing.