May 23, 2025 | 22:45 GMT +7
May 23, 2025 | 22:45 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
May 23, 2025 | 22:45 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918

Dr. Do Tien Phat - Head of Plant Cell Technology Department, Institute of Biotechnology (Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology). Photo: Tung Dinh.
From traditional mutagenesis-based breeding methods to gene transfer techniques, Vietnamese scientists have now applied the CRISPR/Cas system, a method that allows for precise additions or deletions of gene segments, customization of target gene expression levels, and intentional modifications to chromosome structures. The CRISPR/Cas system is regarded as the most effective and accurate tool in plant breeding today.
Dr. Do Tien Phat, Head of the Plant Cell Technology Department at the Institute of Biotechnology (Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology), leads a group of scientists who have successfully developed and applied the CRISPR/Cas system in basic research. Their findings have been published in numerous prestigious international journals, showcasing their accomplishments. Some of their research has also been registered for intellectual property protection, with promising potential for practical applications in production.
In basic research, the team at the Institute of Biotechnology has developed systems to quickly assess the effectiveness of gene-editing constructs. In collaboration with a research group at Vietnam-France University (USTH), they have applied the CRISPR/Cas9 system to study the function of genes related to root hair formation in cucumber roots, as well as genes that influence root development and phosphorus absorption capacity in rice.
In terms of application, biotechnology researchers have partnered with experts from the University of Missouri (USA) and the IPK Research Institute (Germany) to successfully use the CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing system. They have created targeted mutations in genes related to the biosynthesis of indigestible sugars in soybean plants, reducing the levels of these sugars in Vietnamese soybean varieties. This reduction enhances digestion and improves the nutritional value of soybean products. The research has been patented by the Intellectual Property Office of the Ministry of Science and Technology.
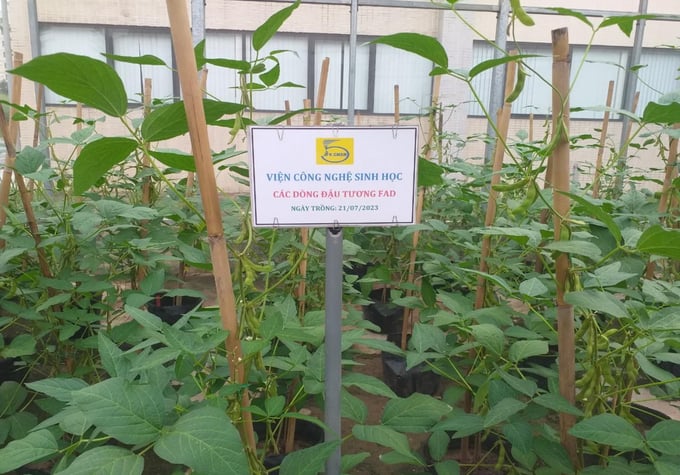

Improved bean varieties are tested in greenhouses over several seasons to evaluate genetic stability. Photo: VAST.
Specifically, the application of gene editing to induce mutations in the DT26 soybean variety has resulted in a new bean variety with a 30-50% reduction in indigestible sugar content. This new variety is currently undergoing greenhouse testing over several seasons to evaluate its genetic stability. In the near future, scientists plan to conduct field trials under controlled conditions to further assess its performance.
As part of a research project funded by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development, the biotechnology research team, in collaboration with the Agricultural Genetics Institute, developed mutant soybean lines with an Omega-9 (oleic acid) content exceeding 80%, a significant increase compared to the original variety's 20%. This achievement aligns with recent breakthroughs in gene-edited soybean varieties from the United States and China, which have already been commercialized.
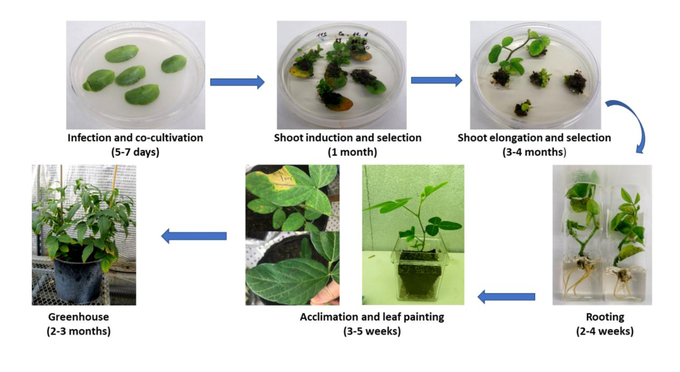
Building on this success, the research team continued to employ gene-editing technology to create multi-gene mutations in the DT26 soybean variety, resulting in plant lines resistant to powdery mildew.
In addition to improving crop resistance, the research team also focused on enhancing the nutritional quality of agricultural products. By creating a targeted mutation of the bZIP1 gene in tomato plants, they produced mutant tomato lines with significantly higher sugar content in the fruit. Furthermore, the amino acid content in these fruits showed a marked increase compared to the original variety.
“Most importantly, we have observed that the inherent agronomic characteristics of soybeans have remained stable across many generations,” affirmed Dr. Do Tien Phat. He is optimistic that these new varieties will soon be ready for practical application in agricultural production.
Several promising products have been developed as raw materials for further research and for direct use in production. These achievements pave the way for future collaborations between the Institute of Biotechnology and partners in the areas of research, technology development, and product commercialization.
With their extensive collaborations both domestically and internationally, researchers at the Institute of Biotechnology have successfully developed and mastered genome editing technology through the CRISPR/Cas system.
The groundbreaking advancements in gene editing at the Institute of Biotechnology, particularly through the CRISPR/Cas system, have marked a significant milestone for Vietnam's agricultural sector. These innovations not only promise higher yields and better food quality but also position Vietnam as a key player in global biotechnology research. As these achievements move from the lab to the field, they offer exciting opportunities for sustainable production and international collaboration in the future.
Translated by Quynh Chi

(VAN) The People's Committee of Tra Vinh province has approved an adjustment to the investment policy for the Green Hydrogen Plant project, increasing its area to approximately 52.76 hectares.
![Reducing emissions from rice fields: [2] Farmers’ commitment to the soil](https://t.ex-cdn.com/nongnghiepmoitruong.vn/608w/files/news/2025/05/05/dsc08881jpg-nongnghiep-140632.jpg)
(VAN) Clean rice cultivation model in Thuong Tan commune, Bac Tan Uyen district, is assisting local residents in achieving sustainable agriculture by substantially reducing costs, increasing productivity, and protecting the environment.

(VAN) At the conference to disseminate Resolution No. 68, AgriS introduced its digital agricultural ecosystem and reaffirmed its commitment to accompanying the Government in promoting private sector development and sustainable agriculture.

(VAN) 'Blue Ocean - Blue Foods' initiative is designed to restore marine ecosystems and establish sustainable livelihoods for local communities by cultivating a minimum of 1,000 hectares of cottonii seaweed in the first three years.
/2025/05/21/4642-3-112707_603.jpg)
(VAN) The V-SCOPE project has made direct contributions to three out of six pillars of the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership between Vietnam and Australia.

(VAN) Facing the threat of rabies spreading to the community, Gia Lai province urgently carries out measures to vaccinate dogs and cats on a large scale.

(VAN) Disease-free livestock farming not only protects livestock herds but also stabilizes production and livelihoods for many farmers in Tuyen Quang.