June 18, 2025 | 01:01 GMT +7
June 18, 2025 | 01:01 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
June 18, 2025 | 01:01 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
Cuu Long Delta is Vietnam’s most favorable place to produce food. Following that logic, food security is considered to have a stable and plentiful amount of rice. Accordingly, rice areas, crop numbers and yields must be maintained at a high level. Any impacts on rice yield such as flood water, saline intrusion in the coastal dry season need to be solved immediately.
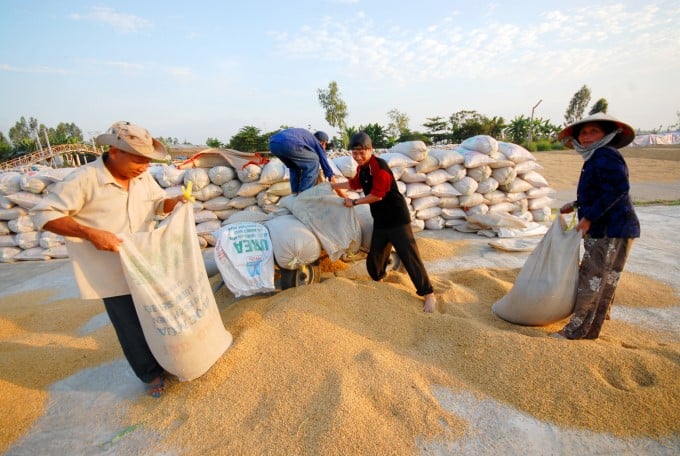
Cuu Long Delta produces about 25 million tons of rice annually, exports more than half of it, mostly of low value and we think that is food security. But in the food security rankings, Singapore ranks number one in the world and Vietnam only ranks 54/113 despite being the top largest rice exporter in the world. It is clear that the food security strategy needs to be reconsidered.

Cuu Long Delta produces about 25 million tons of rice annually, and exports more than half of it. Photo: Le Hoang Vu.
As defined by FAO, food security is “Having food available at any time, physically and economically accessible, sufficiently in quantity, in safety, and in nutrition, to meet the needs of eating appropriately for a positive and healthy life”.
Thus, food security is not about self-production, but about accessibility by the economy, buyable using money. In order to prevent an unexpected crisis or crisis, it is necessary to have a backup source. It will be more secure if the backup source can be self-produced but not necessarily so, as it can be purchased to reserve.

Rice harvest in Cuu Long Delta. Photo: Le Hoang Vu
It should be emphasized that one aspect of food security is sustainability, because food security is not just for one year, ten years, twenty years but for sustainability for generations to come.
For a long time, our food security strategy mainly focuses on self-production, tightly concentrated in rice, using the “high input - high output” method. Consequently, our rice yield is multiple times higher than other ASEAN countries (Vietnam’s rice yield was at 5.6 tons/ha in 2016, 2 times higher than Thailand, 1.5 times higher than India), but the amount of fertilizers and pesticides used was also higher, leaving behind environmental and health implications.
With this approach, the land was exhausted. Accompanying with the goal of maximizing rice production is a huge water-regulating system that disturbs the natural system, cutting contact between the river and the sea, causing them to gradually degrade. Land, rivers, and seas have to bear an enormous amount of fertilizers, pesticides, and pollution from agriculture.
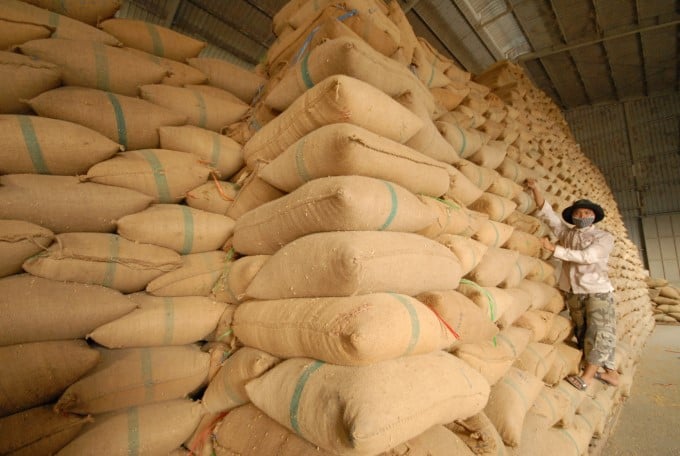

Also, usually, when we think of food security, we often think about having a food stockpile in case something goes wrong. Photo: Le Hoang Vu.
Also, usually, when we think of food security, we often think about having a food stockpile in case something goes wrong, but the storage in the warehouse is not long because, after a few years, they have to leave the warehouse and be replaced with new food. A safer, longer-term storage place is actually in the health of the soil and water, as the strategy of maintaining high rice yields will not guarantee the certainty of long-term food security.
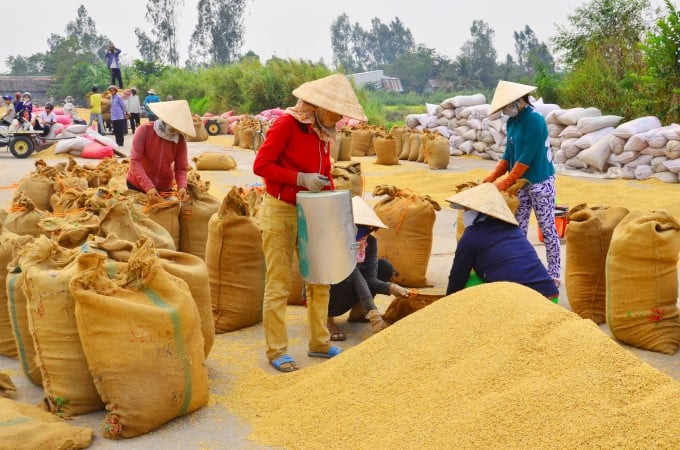

In order for food security not to be instant, but in the long term, agriculture needs to be transformed in nature, not just superficial restructuring. Photo: Le Hoang Vu
In order for food security not to be instant, but in the long term, agriculture needs to be transformed in nature, not just superficial restructuring.
Firstly, reduce the number of intensive agriculture, nourish the soil, and ensure sustainable production capability for the land.
Secondly, aim at a gradual strategic shift, not pursue the export of cheap raw agricultural products which bases solely on volume strength.
Thirdly, the total rice area should not be tightly kept. Instead, it should be more flexible, keeping only the agricultural area, and there should be more than rice production on that agricultural area, as long as it is food production.
The agriculture shift should base on respect for the natural law in line with the Government's Resolution 120 on the Cuu Long Delta. Specifically, interventions that go against the laws of nature should be limited, because even if achievements can be obtained in short term, in the long run, things that contradict the law of nature will be fragile, and those that conform to the laws of nature will be more solid.
Translated by Samuel Pham

(VAN) According to the Binh Thuan Department of Industry and Trade, in the first five months of 2025, Binh Thuan's dragon fruit export turnover increased by 20.65% compared to the same period last year.

(VAN) EU countries on Thursday gave final approval to new tariffs on fertilizer imports from Russia, a move aimed at cutting off revenue that could support Moscow’s war in Ukraine, despite concerns from European farmers.

(VAN) The working delegation from the Ministry of Agriculture and Environment conducted an important trip to the Netherlands to strengthen strategic partnerships and sustainable development in the agricultural sector.

(VAN) The letter ‘A Plea from the Ocean’ not only evokes emotion but also awakens the human conscience to the responsibility of protecting life on Earth.
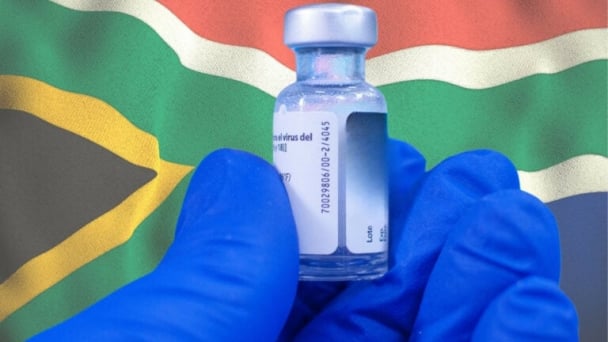
(VAN) The Department of Agriculture in South Africa has announced the country’s first mass vaccination of poultry to prevent local birds from contracting avian influenza.

(VAN) Establishment of the Mekong Delta Regional Agricultural Linkage Center, aiming for a closed value chain, deep processing, trading platforms, and international market connectivity.

(VAN) Gia Lai province has recently recorded 460 rare species of animals and plants, contributing to forest conservation and biodiversity planning in the region.