May 30, 2025 | 17:36 GMT +7
May 30, 2025 | 17:36 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
May 30, 2025 | 17:36 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
During their inspection of plant diversity in the northern caves, Associate Professor Dr. Do Van Truong and his colleagues from Vietnam National Museum of Nature and Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology discovered and described 3 new plant species to the world science (Bredia bullata, Microchiriata minor, Primulina crassifolia) and added 6 species to plant system of Vietnam (including Aristolochia austroyunnanensis, Brandisia kwangsiensis, Euchresta tubulosa, Henckelia nanxiensis, Primulina jingxiensis, Spiradiclis baishaiensis).
Scientists collected plant specimens from 33 caves across 8 provinces in Northern Vietnam: Ha Giang, Tuyen Quang, Cao Bang, Lang Son, Hoa Binh, Son La, Ninh Binh, and Thanh Hoa.

Some newly discovered and additional species for the cave flora of Vietnam. Photo: Research Team.
The research team identified 337 species belonging to 142 genera and 63 families of cave-dwelling plants in Northern Vietnam. Among these, the group of ferns (Pteridophytes) includes 53 species (accounting for 15.73%), and the group of flowering plants (Angiospermae) includes 284 species (accounting for 84.27%).
The research also identified 221 species with practical uses, such as ornamental plants, medicinal plants, wood and fuel sources, and food. Notably, 40 species possess rare genetic resources. Following the discovery, the research team developed a morphological and ecological database for 337 plant species and a molecular database for 25 endemic or newly discovered and described endemic cave-dwelling plant species in Vietnam.
Associate Professor Truong stated that 25 cave-dwelling plant species in Northern Vietnam have been included in the Red List, with 4 species listed in the Vietnam Red Data Book. The scientists have initially assessed the endangered status and current conservation status of the newly discovered plant species in the caves of Vietnam.
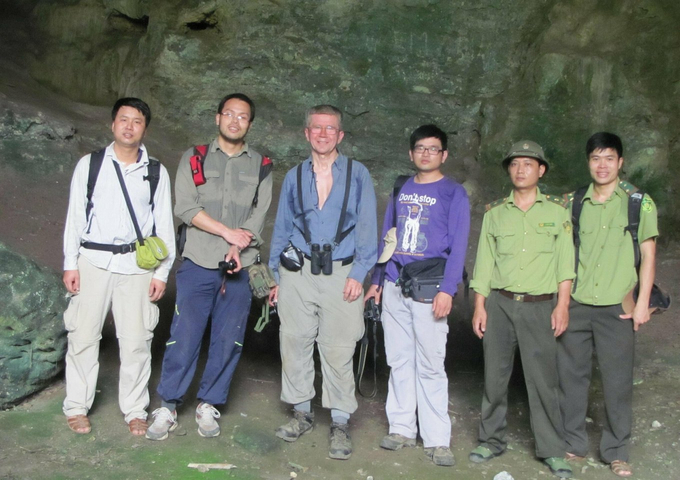

Associate Professor Dr. Do Van Truong (left) and colleagues conducting field surveys in the caves of Northern Vietnam. Photo: Research Team.
The cave system in Vietnam holds unique biological values. Assessing the diversity of cave-dwelling plants provides a scientific foundation for developing conservation programs and sustainably managing the genetic resources of rare, endemic, and valuable plant species. This contributes to socioeconomic development and the restoration of forest ecosystems on limestone mountains in Vietnam.
Associate Professor Dr. Truong and the research team will continue to investigate the plant species composition in the limestone caves of Central Vietnam. He emphasized that researching and conserving endemic and rare plant species in limestone areas and caves is crucial for utilizing unique genetic resources. This serves as a basis for restoring cave landscapes, which supports conservation efforts and tourism development.
Translated by Linh Linh
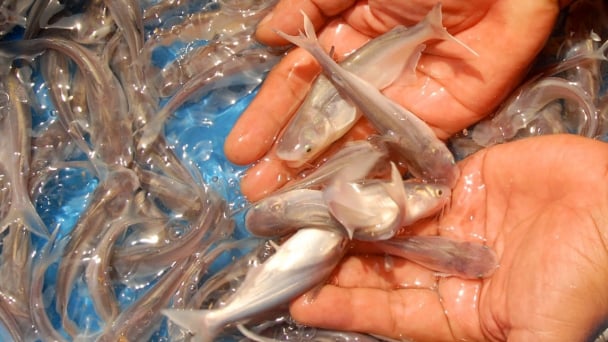
(VAN) Vaccinating juvenile pangasius helps reduce disease, antibiotic use, and farming costs, increasing profits for export-oriented farmers in An Giang.

(VAN) Due to a limited supply of workforce and competitive recruitment requirements, businesses struggle to retain talented veterinary human resources.

(VAN) WOAH’s guidance aims to mitigate disease risks through a One Health approach that balances economic, conservation, and public health interests.

(VAN) Ms. Nguyen Thi Dung, Deputy Director of Ngoc Hoang Cooperative, shared about the journey of bringing dragon fruit to Europe, achieving annual revenues in the billions of VND.

(VAN) Bamboo products from Thang Tho Bamboo Cooperative have reached many countries around the world, while also creating jobs for local workers.

(VAN) The Management Board of Con Dao National Park reported that a green sea turtle, tagged in the Philippines, has traveled thousands of kilometers to lay 84 eggs on Bay Canh Islet.

(VAN) Green technology is paving a new path for sustainable aquaculture in the Mekong Delta in particular and across the country in general, helping reduce emissions and adapt to climate change.