June 4, 2025 | 17:26 GMT +7
June 4, 2025 | 17:26 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
June 4, 2025 | 17:26 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918

About 11.5bn lbs of soyabean oil will be used to make biofuels in the US this year, according to the Department of Agriculture. Photo: Getty
Fuel refiners including Marathon Petroleum and ExxonMobil are adding “renewable diesel” to their product mix in response to government incentives for cleaner fuels. The raw materials are typically edible oils extracted from plants or animal fat.
The push has alarmed food companies coping with record prices for many edible oils this year. But the energy sector is just whetting its appetite in the vegetable oil market, according to analysts and public announcements from refining companies.
“We support renewable fuels and the green agenda, but soyabean oil [prices] have tripled. Our members are worried that they may not be able to buy any oil,” said Robb MacKie, chief executive of the American Bakers Association.
The trade group, which counts Krispy Kreme, Bimbo Bakeries USA and Pepperidge Farm as members, recently met officials at the US Environmental Protection Agency to urge lower federal mandates for biofuels.
Food groups have long opposed biofuels targets in the US, notably over corn ethanol mandates that were sharply raised in 2007. This time the focus has shifted to the feedstocks for diesel-type fuels used in heavy-duty vehicles.
In food and agricultural circles, “it’s become the diesel vs doughnuts debate as food and fuel compete for that oil”, said David Widmar, an agricultural economist and consultant.
The US Department of Agriculture predicts the price of soyabean oil will average 65 cents a pound this year, more than double the price of two years ago.
Krispy Kreme, the New York-listed doughnut company, last month cited “significant commodity cost pressure, particularly from edible oils” as it raised prices. “I must admit the commodity pressure in the short-term has just been quite extraordinary,” chief financial officer Josh Charlesworth told analysts.
Tensions are at their highest in the US, where federal policy and low-carbon fuel mandates in states such as California are driving heavy investment in renewable diesel production capacity.
The amount of soyabean oil used to make biofuels in the US is expected to total 11.5bn lbs this year, up by a third from 2019 and more than 45 per cent of domestic soyabean oil consumption, according to USDA estimates.
The US Energy Information Administration forecasts that renewable diesel production capacity will reach 5.1bn gallons a year by 2024. While a fraction of petroleum refining output, it would be up from 600m gallons at the end of 2020.
By 2028 the US renewable diesel and biodiesel industry would need almost 30bn lbs of feedstocks including soyabean oil, canola oil, used cooking oil and grease, predicts commodity broker StoneX.
Oil companies have flocked to renewable diesel markets over the past two years. Last month, ExxonMobil proposed a renewable diesel investment in Canada. Independent oil refiners Marathon, Phillips 66 and HollyFrontier are also pursuing projects.
Some oil companies are adding agricultural processing to their assets. Marathon and Archer Daniels Midland have formed a joint venture to crush soyabeans in the farmlands of North Dakota, sending the soyabean oil to a new renewable diesel plant that Marathon is developing.
Chevron last week said it planned to invest $600m in a soyabean joint venture with Bunge, the world’s largest oilseed processor, to create what the two companies called a “reliable supply chain from farmer to fuelling station”.
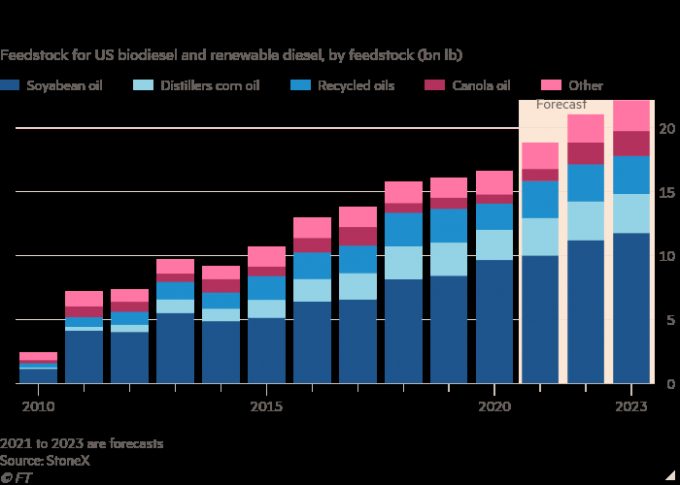
Biofuels to drive up demand for edible oils
Jeremy Baines, US president of Finland-based Neste, the world’s largest biodiesel refiner, said renewable fuel demand from airlines and road transport would only grow. “My expectation is that we continue to see the demand for renewable fuels, whether it’s in the skies, whether it’s on the roads,” he said.
However, there is some evidence that the surge in feedstock prices has slowed renewable diesel’s momentum, at least temporarily.
David Lamp, the chief executive of CVR Energy, a US refiner controlled by the investor Carl Icahn, told analysts last month the company had hit pause on a new renewable diesel project in Oklahoma because of the “spike” in feedstock prices, which he blamed on the start up of a pair of new plants in the US.
Sky-high vegetable oil prices are also having a global impact, recently forcing Brazil and Argentina to reduce biodiesel mandates and putting Indonesia’s fuel-blending plans at risk, said Michael Magdovitz, analyst at Rabobank.
In future, demand for biofuels in the US is likely to mean that the country’s trade flows for edible oil will shift, said Arlan Suderman, chief commodities economist at StoneX. “The US will be more and more of a net importer than a net exporter,” he added.
Baines acknowledged that growth in biofuel production was influencing agricultural markets. “Will there be some short-term pricing impact? Yes, there will be, just like there’s been in the petroleum world as well. But I think one of the advantages of renewables, is that this is becoming a long-term business,” he said.
A long-term view offered little comfort for MacKie. He said his members at the American Bakers Association are being told by suppliers that they could run short of vegetable oil stocks by the end of the year.
“It’s going to get worse before it gets better. We have some members who are very concerned,” he said. “Let’s just pause so growers can grow more beans.”
(Financial Times)

(VAN) Vikas Rambal has quietly built a $5 billion business empire in manufacturing, property and solar, and catapulted onto the Rich List.

(VAN) Available cropland now at less than five percent, according to latest geospatial assessment from FAO and UNOSAT.

(VAN) Alt Carbon has raised $12 million in a seed round as it plans to scale its carbon dioxide removal work in the South Asian nation.

(VAN) Attempts to bring down the price of the Japanese staple have had little effect amid a cost-of-living crisis.

(VAN) Fourth most important food crop in peril as Latin America and Caribbean suffer from slow-onset climate disaster.

(VAN) Shifting market dynamics and the noise around new legislation has propelled Trouw Nutrition’s research around early life nutrition in poultry. Today, it continues to be a key area of research.

(VAN) India is concerned about its food security and the livelihoods of its farmers if more US food imports are allowed.