June 17, 2025 | 03:35 GMT +7
June 17, 2025 | 03:35 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
June 17, 2025 | 03:35 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
According to the Department of Crop Production, cassava is one of the crops included in the list of national key crop products, playing an important role in agricultural and rural economic development and contributing to improving the lives of farmers.

Deputy Minister of Agriculture and Rural Development Hoang Trung: Promote the cassava industry to develop stably, effectively, and sustainably; build a close linkage between production, processing, and consumption of products to create high economic value. Photo: Tran Trung.
Currently, the whole country has over 40 cassava-growing provinces and cities, concentrated in five main key regions, including the Northern Midlands and Mountainous Region, North Central Coast, South Central Coast, Central Highlands, and Southeast, with an area of 520,000–550,000 ha. Productivity reaches 19–20 tons/ha, and output reaches over 10 million tons of fresh tubers.
Regarding processing, the country currently has over 140 cassava starch processing factories, with a total design capacity of 13.4 million tons of fresh tubers/year and a total actual capacity of 9.3 million tons/year. Factories are mainly distributed in the Southeast region, with about 70 factories, most of which are methodically invested and are in the process of updating and improving technology for processing cassava products.
"It can be seen that the production, processing, and consumption of cassava in recent times have achieved remarkable results in both output and export turnover value. Currently, cassava is not a crop to eradicate hunger and reduce poverty as previously envisioned but has developed into a multi-value crop with high economic efficiency and an export turnover that always remains stable at USD 1–1.4 billion," emphasized Ms. Nguyen Thi Thu Huong, Deputy Director of the Department of Crop Production.
According to the Plant Protection Department, in June 2017, cassava mosaic disease (CMD) was discovered to cause damage in Tan Ha commune, Tan Chau district, Tay Ninh province and spread throughout the country. At its peak in 2021, the total infected area was 120,686 ha, of which 30,035 ha were severely infected.
Thanks to the attention and direction of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (MARD), specialized agencies, and local governments in disease prevention and control, along with the support of international organizations, in recent times, many new scientific and technical advances in varieties, fertilizers, pesticides, farming techniques, etc., have been researched and gradually applied to production.
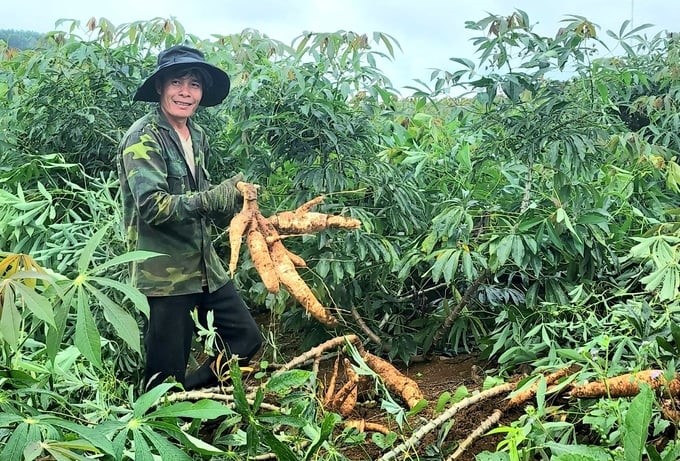

Cassava is a multi-value crop, playing an important role in agricultural and rural economic development and contributing to improving the lives of farmers. Photo: Le Hoang Vu.
Many CMD-resistant cassava varieties, such as HN3, HN5, HN36, HN97, HN80, and HN1, have been circulated and developed in production. Accompanying that are disease-free breeding processes, CMD prevention and control processes, and cassava farming processes, which have also been developed and applied in actual production.
Currently, the country has about 5,500 ha of cassava that have been planted with disease-resistant varieties, mainly concentrated in the provinces of Quang Ngai, Binh Thuan, Gia Lai, Dak Lak, Tay Ninh, Dong Nai, etc. In 2023, the total infected area was 83,734 ha, and the seriously infected area was 20,956 ha, down more than 30% compared to 2021.
"The source of CMD is mainly due to the use of diseased cassava varieties for planting, while the source of cuttings transported from one area to another, especially from diseased areas to non-infected areas, is not controlled. Cassava yield in newly infected areas is only slightly reduced, but if infected varieties are used for the next crop, the yield will decrease sharply or not be harvested at all. Therefore, controlling the spread of diseases by infected varieties and using disease-free and disease-resistant varieties are the two most important issues today," said Mr. Nguyen Quy Duong, Deputy Director of the Plant Protection Department.
The role and position of cassava in Vietnam's agricultural map have been clearly established. To support the cassava industry, MARD recently approved the project "Sustainable development of the cassava industry until 2030, with a vision to 2050."
Accordingly, the target is that by 2030, the country's fresh cassava output will reach about 11.5–12.5 million tons, of which fresh cassava output used for deep processing of some products (starch, ethanol, MSG, etc.) accounts for about 85%. The cassava growing area using varieties that meet quality standards will reach 40–50%, and the cassava growing area applying sustainable farming processes will reach 50%. The export turnover of cassava and cassava products will reach USD 1.8–2.0 billion.

The cassava industry sets an export target of USD 2 billion by 2030. Photo: Tran Trung.
With a vision to 2050, Vietnam's cassava industry will continue to develop sustainably, and 70–80% of the cassava growing area will apply sustainable farming processes. Fresh cassava output used for deep processing of some products (starch, ethanol, MSG, etc.) accounts for over 90%; the export turnover of cassava and cassava products reaches about USD 2.3–2.5 billion.
To effectively implement the project, at the conference, delegates participated in discussions and proposed a number of solutions for the project, such as: the State needs to build mechanisms and policies to develop the cassava industry; review and promulgate legal documents related to cassava production, processing, and consumption.
Plan stable cassava raw material areas; develop high-yield and sustainable farming measures, especially in poor and sloping lands; and organize communication to clarify the role of cassava and the cassava industry. At the same time, well implement measures to prevent and control harmful organisms on cassava, especially CMD, through the main measures of planting disease-resistant and disease-free varieties.
In parallel with that, promote the application of circular processing technology, utilizing all by-products in cassava processing to increase economic efficiency and protect the environment, aiming to open more markets, increase market shares, diversify types of consumer goods, and export cassava and cassava products.
Speaking at the conference, Deputy Minister of Agriculture and Rural Development Hoang Trung said that in recent years, the cassava industry has achieved many significant achievements. It can be mentioned that export turnover always ranks at the top among agricultural products, and cassava productivity is the 5th highest among the top 10 cassava-producing countries in the world. Some CMD-resistant cassava varieties have been developed in cassava-growing areas throughout the country; many cassava processing technologies, such as the production of modified cassava starch, have been applied in many cassava factories in Vietnam.
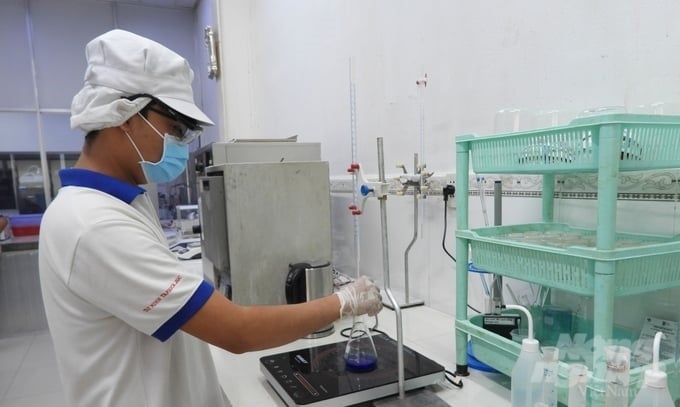

Cassava businesses promote the research and application of circular processing technology. Photo: Tran Trung.
However, to develop the cassava industry to deserve its position in the coming time, there are still many existing problems that need to be resolved. For example, the cassava production is not sustainable. Specifically, the production capacity and scope of using CMD-resistant varieties are still low. Farming techniques have been researched but have not specialized in the specificity of each ecological region and farming condition. Production linkage is not close; infrastructure investment in raw material areas for growing cassava is still limited; and the mechanization rate in cassava production is still low.
Policies to encourage the development of the cassava industry are lacking. Many localities have not really participated and have not included cassava in local development plans and resolutions as a premise for investment and development of this industry. The export market depends largely on China but has not expanded to other markets that also have many advantages in terms of tax incentives, such as the EU market.
"After this conference, I suggest all levels, branches, local governments, businesses, and associations jointly implement the agreed contents to promote the cassava industry to develop stably, effectively, and sustainably; build a close linkage between production, processing, and consumption of products to create high economic value and contribute to creating jobs, eradicating hunger and reducing poverty, and improving the lives of people in rural areas; improve the value of export turnover; and protect the environment," Deputy Minister Hoang Trung emphasized.
Translated by Thu Huyen

(VAN) Noting risks, report examines impacts of avian influenza, changing trade patterns since 2022, fish fraud, and shipping industry’s net-zero goals.

(VAN) Mr. Tran Quang Bao, General Director of the Forestry and Forest Protection Department, met and worked with the International Wood Products Association to promote cooperation in the field of timber trade.

(VAN) China's outbound shipments of rare earths in May jumped 23% on the month to their highest in a year, though Beijing's export curbs on some of the critical minerals halted some overseas sales.

(VAN) To sustain capital flow, administrative reform alone is not enough; what farmers truly need is an ecosystem where both government and businesses grow together in support.

(VAN) Vietnam and the United States are proactively working together, each in their own way, to ensure that every container of agricultural goods carries not just products, but also long-term trust and value.

(VAN) Stores have started selling rice from the government’s stockpile to feed demand for the staple.
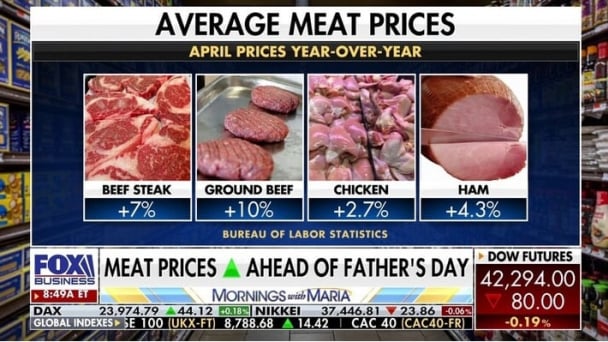
(VAN) Omaha Steaks CEO says rebuilding cattle herds will take about a year to ease price pressures.