June 13, 2025 | 10:00 GMT +7
June 13, 2025 | 10:00 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
June 13, 2025 | 10:00 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
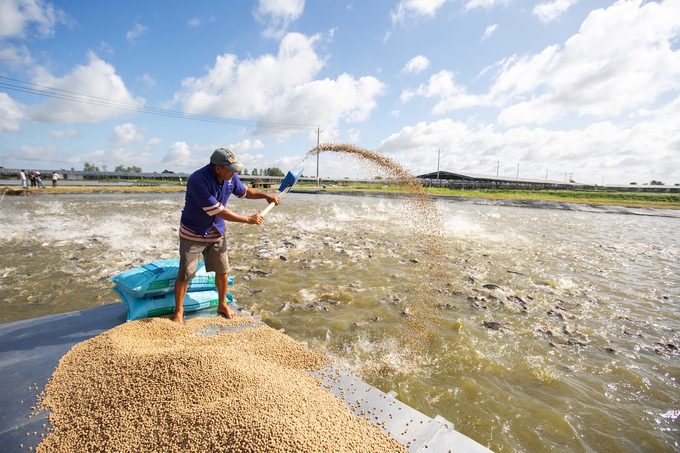

The number of catfish reduces up to 30 - 50% during the commercial farming stage. Photo: ACIAR.
One of the primary goals of the project is to strengthen research capacity for in-country research teams. Researchers had the opportunity to engage in value chain research training, increase their knowledge of social research and data collection skills, and interact with businesses and stakeholders.
Teams were also trained in foresighting techniques, which involve risk analysis by visualizing possible future developments in catfish supply chains.
Following the training, value chain research tools were developed and tested in preparation for data collection scheduled for July and August 2024. The primary research objective is to assess key value chains in the catfish industries of Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos. Given the important roles that both men and women play in catfish processes, literature reviews on gender were conducted to inform the research.
In May 2024, the Adelaide University’s Centre for Global Food and Resources held an in-person workshop with country teams to identify high-value catfish chains, assess progress, and agree on the value chain approach, focusing on Vietnam’s Mekong Delta. Each country finalized key catfish value chains for inclusion in research activities.
Initial stakeholder meetings and interviews were conducted with key informants along the supply chain. Physical and monetary losses were documented from catfish broodstock to fingerlings, through the grow-out stage, transportation, processing, and consumption. These losses were quantified in monetary terms, and other areas of loss were also documented, indicating significant losses throughout the catfish industries.
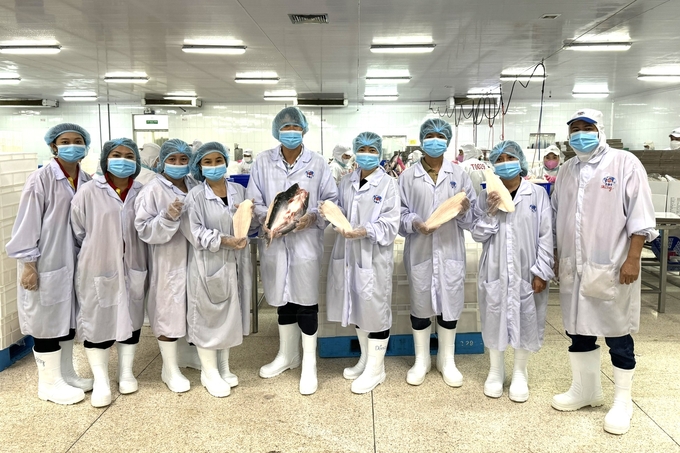
Vietnamese researchers visit the Sao Mai catfish processing plant in Dong Thap province, February 2024. Photo: Trinh Thi Lan, An Giang University.
As this is preliminary research, a more robust, larger-scale survey will be conducted in July and August to refine the value chain analysis and gain deeper insights into food losses and waste, as well as losses in other supply chains.
However, the preliminary research has revealed significant losses in the supply chain, particularly during the fingerling, grow-out, harvest, transport, and processing stages. Consolidated interviews from fingerling farmers, grow-out farmers, transporters, and factories in An Giang Province in January 2024 provided the following information:
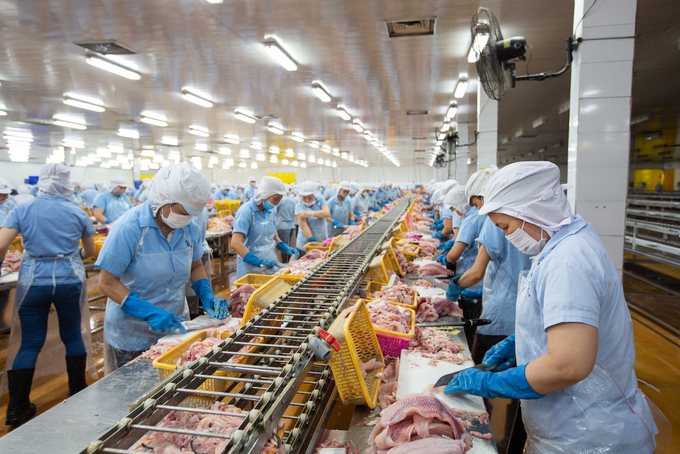

The ACAIAR project team improved understanding of in-plant processing and assessed physical losses. Photo: ACIAR.
The project faced challenges in implementing new concepts like foresighting (risk analysis), value-chain mapping, and gender research in the catfish supply chain. However, comprehensive training from experts in these disciplines has significantly expanded the research capacity of the teams in the three Mekong countries. The interdisciplinary nature and inclusivity of the project have been key to this expansion.
By combining their skills, the research team has capitalized on their technical knowledge about aquaculture and farming, factory processes, and physical loss assessment. Economic and social researchers have brought expertise in economic loss analysis, stakeholder engagement, and collaboration with external partners (government and businesses) to understand food and non-food losses. The project aims to use this knowledge to develop robust interventions that minimize loss and waste in the catfish industries in the Mekong Basin.
The project acknowledges the contributions of research partners, including: Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development of Vietnam, Department of Fisheries (MARD), University of Economics HCM City, University of New England, Swinburne University, The Australian National University, An Giang University - Vietnam National University, Royal University of Agriculture, Cambodia, National University - Laos, Vinh Hoan Company limited, Vietnam-Australia Joint Stock Company, Nam Viet Joint Stock Company, Sao Mai Joint Stock Company, and interviewed farmers, traders, transporters and processors.
Translated by Quynh Chi

(VAN) In Tien Giang, a high-tech shrimp farm has developed a distinctive energy-saving farming model that has yielded promising results.
![Turning wind and rain into action: [3] 300.000 farmers benefit from agro-climatic bulletins](https://t.ex-cdn.com/nongnghiepmoitruong.vn/608w/files/news/2025/06/12/e5a48259d6a262fc3bb3-nongnghiep-125122.jpg)
(VAN) The agro-climatic bulletin has become a valuable tool for farmers in the Mekong Delta. After more than five years of implementation, the initiative is gradually being expanded nationwide.
![Turning wind and rain into action: [2] Providing forecasts to the people](https://t.ex-cdn.com/nongnghiepmoitruong.vn/608w/files/news/2025/06/12/e5a48259d6a262fc3bb3-nongnghiep-103927.jpg)
(VAN) In addition to improving the quality of hydrometeorological forecasts, putting forecast bulletins into practical use is crucial for production and disaster prevention.

(VAN) Blue carbon is receiving attention for its rapid absorption capacity and vast potential. It represents a promising nature-based solution to respond to climate change.
/2025/06/11/3507-1-161904_583.jpg)
(VAN) Seagrass beds and coral reefs serve as 'cradles' that nurture life in the ocean depths, creating rich aquatic resources in Vietnamese waters.
![Turning wind and rain into action: [1] Forecasting for farmers](https://t.ex-cdn.com/nongnghiepmoitruong.vn/608w/files/news/2025/06/11/e5a48259d6a262fc3bb3-nongnghiep-111919.jpg)
(VAN) Weather is no longer just a matter of fate. Forecasts have now become an essential companion for farmers in every crop season.
/2025/06/10/2501-3-082025_983.jpg)
(VAN) Mr. Le Hoang Minh, Head of Vinamilk's Net Zero project, recently shared insights on the integration of production, energy, and technology in Vinamilk’s green transition journey.